Effective Communication in Low Bandwidth Environments: Strategies, Tools, and Best Practices
What is Low Bandwidth Communication?
Low bandwidth communication refers to the exchange of information over a network connection with limited data transfer capacity. In such environments, speed and reliability are often constrained — for example, when users operate in remote regions, during network congestion, or over mobile or satellite connections.
The goal of low bandwidth communication is to ensure that essential data — such as voice, messages, or compressed visuals — can still be transmitted efficiently despite these limitations. To achieve this, communication tools and protocols often use compression, adaptive bitrate streaming, and offline synchronization.
Low bandwidth optimization is crucial for businesses, remote workers, and organizations operating in regions with unstable or expensive internet connections.
Strategies for Low Bandwidth Communication
Operating in a low bandwidth environment requires a deliberate and strategic approach to ensure that communication remains clear, efficient, and reliable. Below are several effective strategies to optimize connectivity and maintain collaboration under constrained network conditions.
1. Use Adaptive Codecs and Compression
One of the most effective ways to improve communication quality on weak connections is by using adaptive codecs such as Opus for audio and H.264 or H.265 for video. These codecs dynamically adjust their bitrate and compression levels in real time based on network conditions.
For example, when bandwidth decreases, they automatically reduce the quality of the stream—such as lowering video resolution or audio sample rate—without dropping the connection. This adaptive behavior minimizes latency, jitter, and packet loss, ensuring that meetings or calls remain intelligible even during bandwidth fluctuations.
In addition, data compression techniques help transmit the same information using fewer bits, which is particularly useful for images, presentations, or large document transfers.
2. Prioritize Critical Data
When network capacity is limited, it’s essential to allocate bandwidth to the most important information. Voice and text should take priority over video or non-essential background processes.
For example, many conferencing tools allow users to switch to audio-only mode, pause video streams, or disable screen sharing to conserve bandwidth. In messaging systems, focusing on text-based communication and avoiding large attachments or multimedia messages helps maintain speed and reliability.
By transmitting only mission-critical data, organizations can sustain essential operations without overloading the network.
3. Leverage Offline and Asynchronous Communication
Real-time communication isn’t always feasible on a poor connection. In these cases, asynchronous tools—such as email, recorded voice or video messages, or shared documents—enable collaboration without requiring a continuous internet link.
For instance, teams can record short video updates and upload them when connectivity is available, or edit shared documents offline that automatically sync once the network stabilizes. To simplify document sharing in these scenarios, a Convert DOC to PDF API can automatically transform files into universally accessible formats, ensuring team members can view and collaborate on content without compatibility issues.
This approach not only saves bandwidth but also improves productivity by allowing people to contribute on their own schedule, reducing the frustration caused by dropped calls or delayed responses.
4. Utilize Caching and Local Storage
Another practical method to reduce bandwidth usage is to store frequently accessed data locally. Caching allows devices to save versions of files, websites, or media so they don’t need to be downloaded repeatedly from the internet.
For organizations using internal systems or intranets, setting up local content delivery networks (CDNs) or edge servers can drastically cut external traffic. This ensures faster access to resources while minimizing network strain—especially beneficial for teams spread across regions with limited connectivity.
Even on a personal level, saving important documents for offline access in collaboration platforms like Google Drive or Microsoft 365 helps maintain workflow continuity.
5. Limit Background Network Usage
Bandwidth can easily be consumed by hidden or automatic processes running in the background—such as software updates, cloud backups, or file synchronization. To preserve connection stability for active communication, these background tasks should be paused or scheduled for off-peak hours.
Users can also disable non-essential apps that continually access the internet or set data usage restrictions within the operating system. This ensures that critical communication tools—like conferencing software or messaging platforms—always receive the majority of available bandwidth.
In managed environments, network administrators can implement Quality of Service (QoS) policies to prioritize communication traffic over non-critical data, ensuring consistent performance for voice and video applications.
Tools for Low Bandwidth Communication
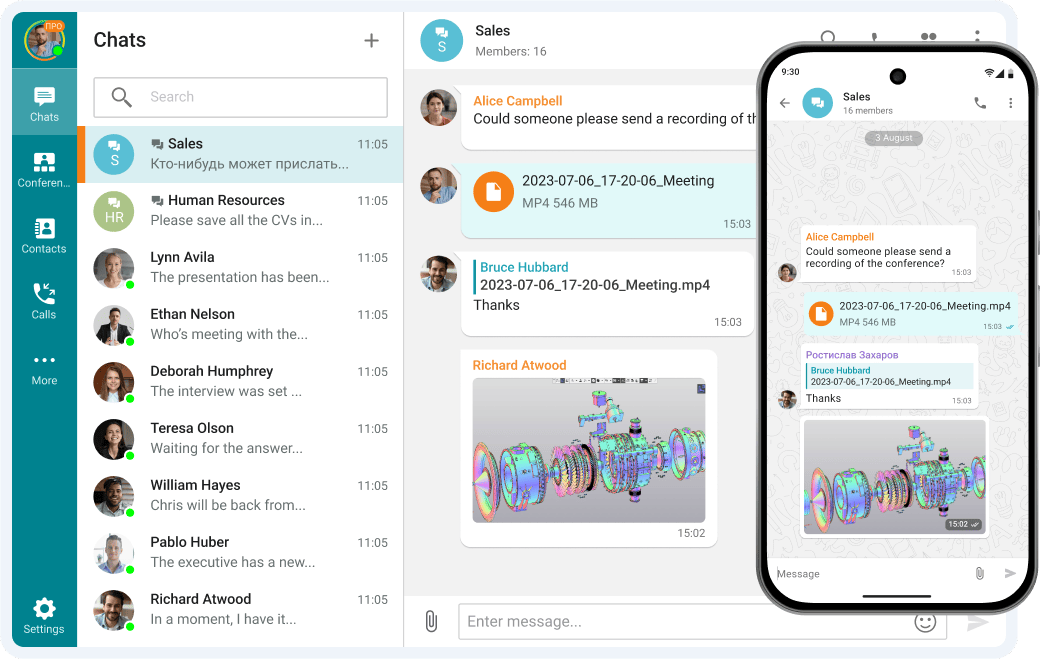
1. TrueConf
TrueConf is a secure video conferencing platform built for both high-quality and low-bandwidth environments. Its proprietary video codecs and adaptive bitrate technology ensure stable performance even on 256 Kbps connections.
Key advantages:
- Optimized for on-premises or private cloud deployment.
- Automatic quality adjustment for audio and video.
- Offline messaging and chat support.
- Low latency and encryption for private networks.
TrueConf’s infrastructure allows organizations to maintain reliable communication channels without depending on external cloud services — ideal for government, education, and enterprise environments.
Take your team communication to the next level with TrueConf!
A powerful self-hosted video conferencing solution for up to 1,000 users, available on desktop, mobile, and room systems.
2. Zoom
Zoom is a widely used cloud-based video conferencing solution that includes several optimizations for low-bandwidth environments. Its adaptive bitrate streaming technology automatically adjusts video resolution and frame rate according to the user’s connection quality. This ensures that participants remain connected even when internet speed fluctuates.
Key advantages:
- Dynamic adjustment of audio and video quality in real time.
- Option to disable video or switch to audio-only mode for minimal data use.
- “Low Data Mode” available on mobile devices to reduce consumption.
- Intelligent background noise suppression to maintain clear communication.
3. Microsoft Teams
Microsoft Teams is an integrated collaboration platform from Microsoft that combines chat, meetings, and file sharing in one interface. It uses adaptive bitrate streaming to optimize performance under low-bandwidth conditions, ensuring that essential communication—especially audio—remains stable even when network quality declines.
Key advantages:
- Automatic prioritization of audio over video during poor connections.
- Intelligent background process management to reduce bandwidth load.
- Offline messaging and file synchronization capabilities.
- Integration with Microsoft 365 for seamless document collaboration, even with limited connectivity.
4. Signal
Signal is a lightweight, privacy-focused messaging application designed for secure and efficient communication, even over slow or unstable networks. By using advanced compression and end-to-end encryption, Signal minimizes data transfer while maintaining strong privacy standards.
Key advantages:
- Highly optimized for low data usage across messages, voice, and video calls.
- Automatic compression of images and attachments.
- Reliable performance on mobile networks and limited connections.
- Strong end-to-end encryption ensuring communication security.
5. Telegram
Telegram is a cloud-based messaging platform known for its speed, flexibility, and efficient data management. It provides users with multiple bandwidth-saving options, including media compression and a dedicated “Low Data Mode,” making it practical for communication in restricted network conditions.
Key advantages:
- Fast and lightweight performance even on 2G or unstable connections.
- “Low Data Mode” for calls and media.
- Cloud storage for instant access to previously downloaded files.
- Option to send text, voice, or compressed media messages.
Related posts:
Real-Time Communication (RTC): The Ultimate Guide
6 Tips on How to Improve Your Video Call Quality
What is Synchronous and Asynchronous Communication?
Managing communication under limited bandwidth doesn’t have to mean sacrificing quality or security. TrueConf enables stable, encrypted, and high-quality communication across any network condition. Its adaptive codecs, on-premises architecture, and intelligent traffic optimization make it one of the most reliable solutions for teams working in bandwidth-constrained environments.
Whether you’re collaborating from a rural office, connecting international teams, or operating in secure government networks, TrueConf ensures that communication remains seamless, clear, and protected — even when every kilobit counts.
Self-Hosted Team Messenger with Video Conferencing!
A cutting-edge team collaboration server with personal and group chats, UltraHD video conferences, and advanced AI-powered features — free for up to 1,000 users!
About the Author
Olga Afonina is a technology writer and industry expert specializing in video conferencing solutions and collaboration software. At TrueConf, she focuses on exploring the latest trends in collaboration technologies and providing businesses with practical insights into effective workplace communication. Drawing on her background in content development and industry research, Olga writes articles and reviews that help readers better understand the benefits of enterprise-grade communication.


Follow us on social networks