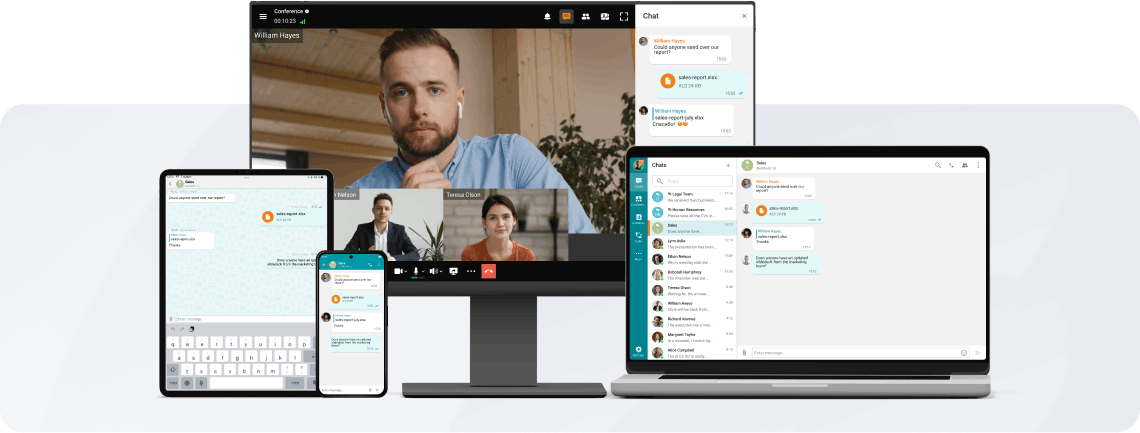
Group Video Conferencing
TrueConf offers reliable group video conferencing for remote teams. Enjoy HD video, secure connections, and powerful collaboration tools.
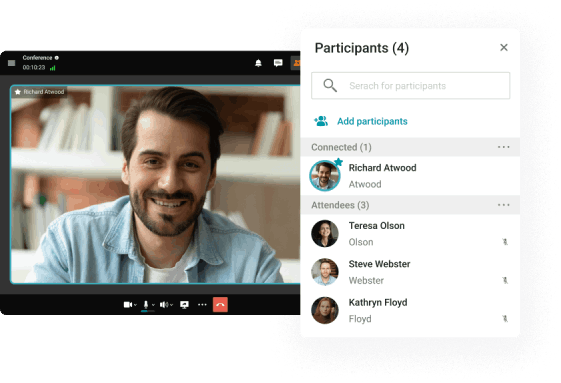
TrueConf offers reliable group video conferencing for remote teams. Enjoy HD video, secure connections, and powerful collaboration tools.
Conferences in 4K
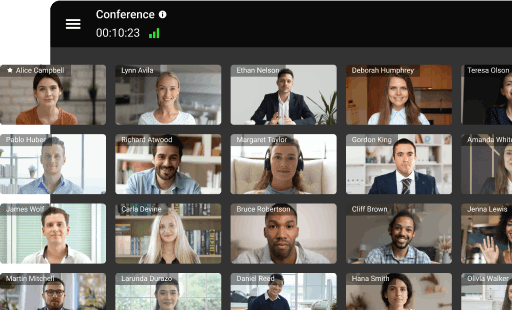
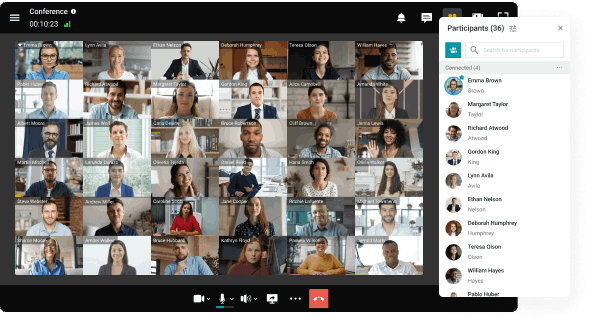
Organize online meetings in 4K for up to 49 participants without time limits.
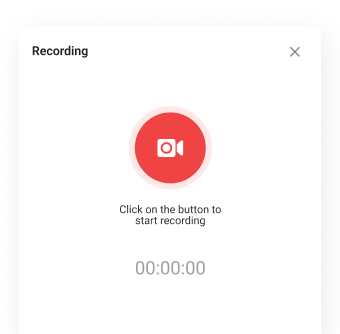
Conference Recording
Take an active part in online meetings without being distracted by taking notes! Record video conferences and share recordings with colleagues.
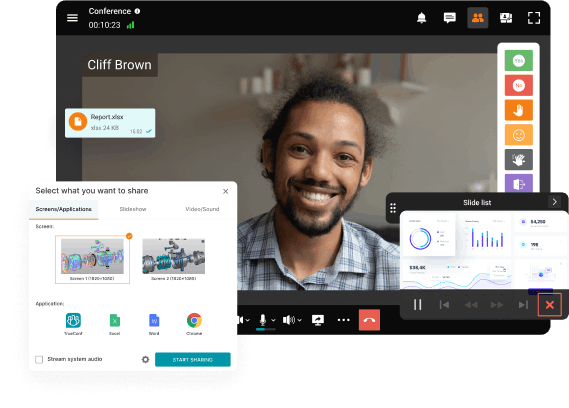
Communicate in the conference chat with other participants, share images, presentations, videos and documents, as well as remotely control your desktop.
Enjoy advanced communication capabilities: participate in video meetings even with external noise, blur, replace and brand the background, and convert conference recordings into detailed transcripts.
Smart Noise Suppression
Blurring and replacing the background
Transcription of the Meetings
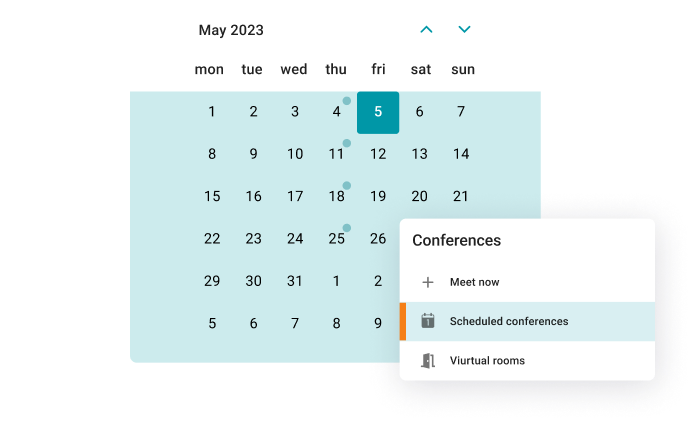
Schedule video meetings in advance — set the date, time, duration, and regular schedule for conferences.
Work in a closed network without an internet connection, data encryption, and full control over communications.
Accept calls and participate in conferences on any device, maintaining the continuity of communication!
Connect to video conferences from third-party endpoints using SIP and H.323 protocols. Register your hardware on TrueConf Server — endpoints will become full-fledged participants of the meeting!
TrueConf Server is a video conference platform for corporate communications that allows webinars to be held by up to a million viewers!
Group or multi-point video conference is a video call meetings, which provides simultaneous participation for several remote users, unlike a point-to-point personal conference, which supports two endpoints only. During a group video conference session users are able to not only see and hear each other, but also to share data and use collaboration tools to work with documents. The purpose of multi user video conferencing is to allow participants who are unable to attend the meeting in person to take part in it remotely.
Group video conferences allow business partners to collaborate on developing new projects; students are able to attend training seminars and lectures remotely; and doctors can advise their patients, as well as upgrade their skills in virtual conferences and symposia. Group video conferences can be symmetric and asymmetric. In symmetric video conferences participants interact with each other fully: they all see and hear each other, having the ability to communicate. Video conferences, in which there is no communication between some of the participants, are called asymmetric. Typically, symmetric video conferences hold up to several dozens of participants, while asymmetric conferences may involve up to a hundred or more remote users.
There are three types of asymmetric video conferences: teleconferences or virtual meetings, video lectures (video seminars) and video broadcasting.
Virtual Meetings
During a virtual meeting (role-based conference) the audience is divided between those who are engaged in two-way communication (they can see, hear and speak at the same time – as a rule these include the host of the video conference and several speakers assigned by him/her) and those who can only see and hear the speakers.
Video Lecture
Video Lecture is a video conferencing session, which involves more interaction between a speaker and a few listeners. In contrast to the virtual meeting mode, where the speaker broadcasts to a wide audience while not being able to see and hear the other participants, in the video lecture mode it is possible to do so. Students, in turn, can see only the lecturer and are not able to communicate with each other.
Video Broadcasting
During a real-time video broadcasting session it is not necessary to receive feedback, as the main task of the speaker is to inform the audience and clearly communicate the main point. Since broadcasting does not imply real-time feedback, the image can be late for a few seconds for the remote participants.
WebRTC (Web Interactive Media): A collaborative-standard framework allowing seamless multimedia functions directly via internet platforms minus traditional extensions. It delivers device-to-browser connectivity for visuals, sound, and file transmission, becoming integral across numerous collaboration frameworks.
SIP (Session Coordination Standard) and H.323: These function as signaling methods deployed to initiate, manage, and conclude interactive media links. They remain vital for compatibility across separate conferencing networks and communication tools.
RTP (Real-Time Streaming Format): A format created for transferring media and visuals across data channels. It maintains smooth transitions and ordered movement of content packets.
MCU (Multipoint Conferencing Core) and SFU (Stream Forwarding Mechanism): These services coordinate group-based conferencing tasks. An MCU compiles multiple audio and media signals into one pathway, whereas an SFU reroutes selected feeds to attendees, increasing overall bandwidth handling and flexibility.