Cloud-based solutions look promising at first glance. The customer does not need to take care of the server infrastructure. There is no need to worry about which vendors’ hardware to choose, how to provide an uninterruptible power supply, organize disk arrays and backup system. Ensuring information security, cooling, security and firefighting in the data center is the responsibility of cloud vendors.
From these advantages comes the main disadvantage of cloud-based solutions: you have no real control over anything. When outsourcing such critical areas as access to computing resources and information security of the company, you must be sure that the services provided to you are as good as those that you could organize on your own equipment.
Characteristics | On-premises | Cloud-based |
|---|
Cost-effectiveness | One-time payment for a license and a flexible technical support package. | Monthly payment for storage, servers, and other infrastructure in addition to limited memory. |
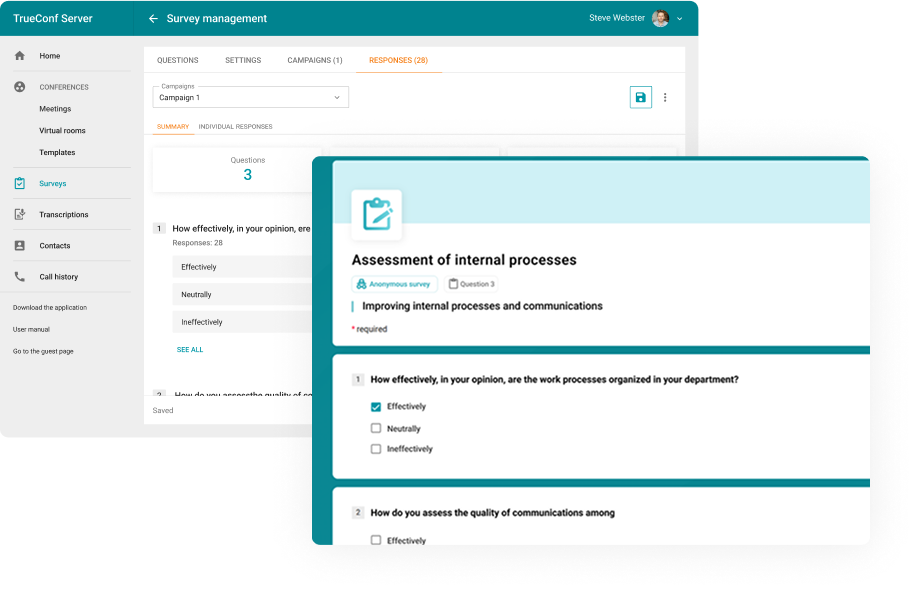
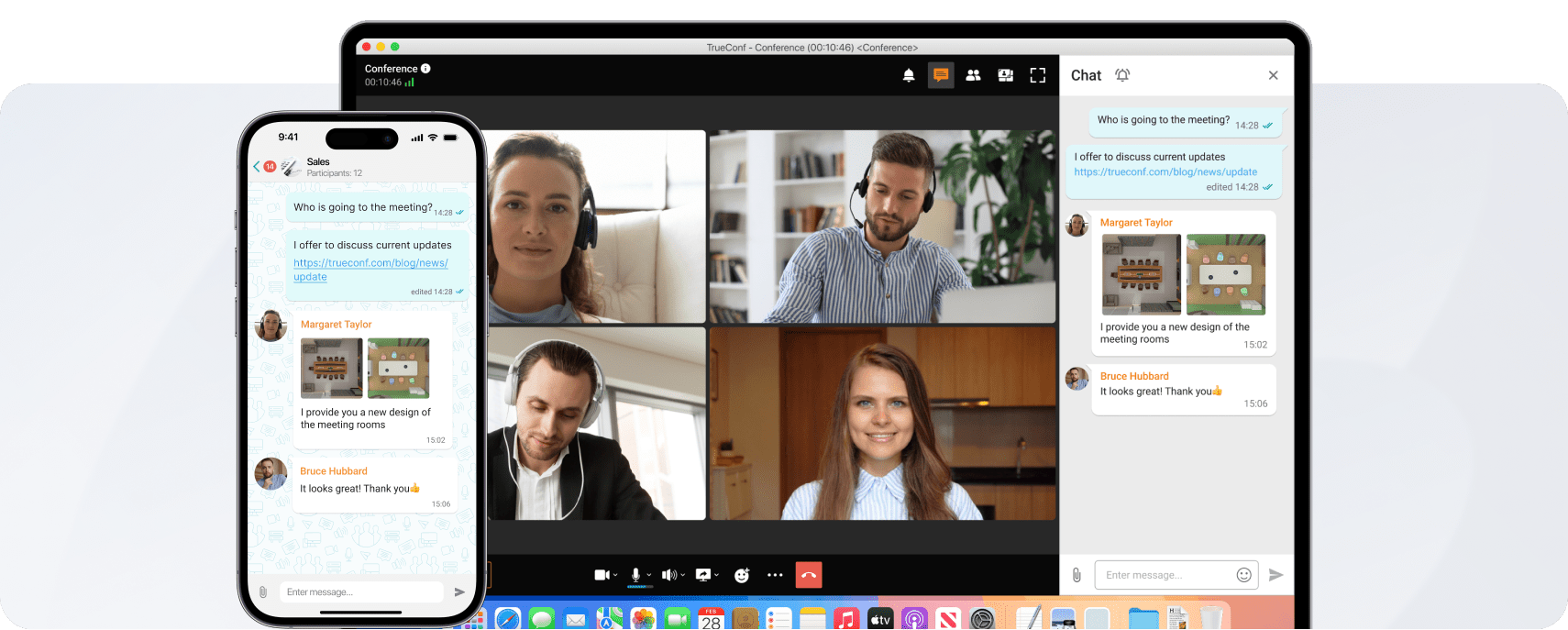
Control and management | Total control and management over all data, which is especially useful when you work in highly regulated industries where privacy is a top priority. | Vendors are the ones responsible for performing software updates. Also, you don’t need an in-house IT team to help out with backups or upgrades. |
Security | On-premise software helps the companies keep the data safe by containing it, while their employees have less access to sensitive information. | The security of many vendors is very sophisticated. They have the facilities and equipment to securely store the data when it is not in use. |
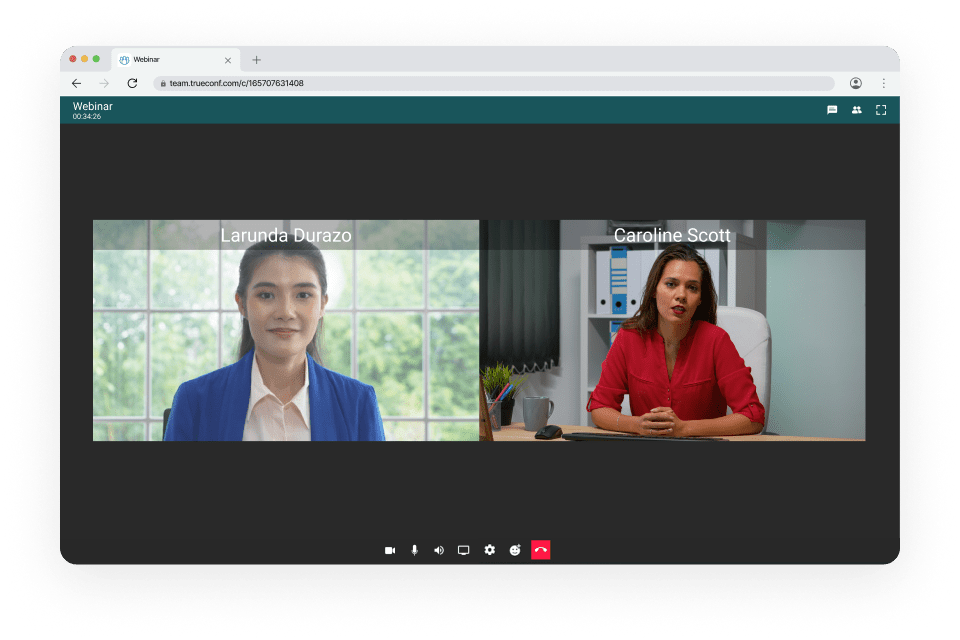
Access | On-premises software can be accessed without an internet connection. This is perfect for places that don’t have reliable internet and where more than one person needs to use it at the same time. | You need to have an internet connection to access your cloud-based assets, but this won’t affect the speed of loading times. But even if you don’t have an internet connection, you can still do all basic actions. |
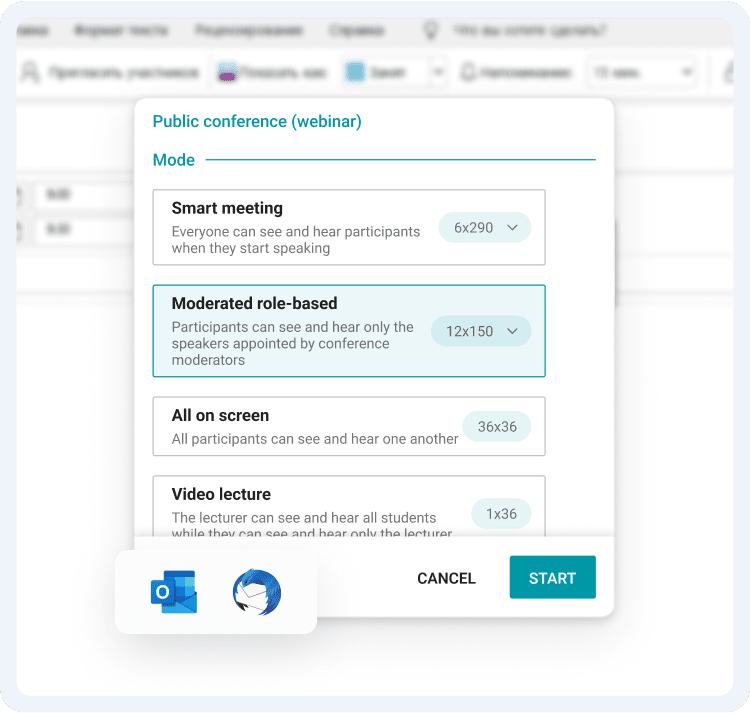
In addition, cloud services often do not allow you to customize your infrastructure flexibly. You will have to choose from existing sets of configurations that may be insufficient or redundant for your needs.
On-premise is a classic model of access to computing resources. It means that the servers on which corporate software is installed are owned by the organization. As in the case of cloud solutions, the advantages here follow from disadvantages, and vice versa. You’ll have to monitor the deployment and maintenance of your server infrastructure, but it will fully meet your requirements. With the on-premises approach, you can control:
• the price/performance ratio of the server infrastructure for optimal efficiency
• organization data privacy
• the competence of the employees maintaining the server
• protection against physical damage to equipment by both natural phenomena and intruders
• recovery time in case of failures.