Verbal Communication Explained
What is Verbal Communication?
Verbal communication is the act of speaking, in most cases the directed expression of ideas or information in words. It is one of the most important forms of exchange. An article published in the International Journal of Business Communication reports that more than half of the communication that takes place in the workplace, almost 55%, is verbal, which means that the importance of language in business cannot be ignored.
Verbal vs. Nonverbal Communication
Verbal communication involves the use of spoken or written words to express thoughts, ideas, or emotions. It includes conversations, speeches, emails, and text messages, where language serves as the main tool for communication.
In contrast, non-verbal communication involves sending information in a communication context without using words, such as the physical movements of the body, facial expressions, various movements, body positions, gaze, vocal characteristics.
Studies have shown that only 7% accounts for the spoken word, while 93% relies on the non-verbal aspect of communication, that is, body language makes up 55% and 38% tone interpretation.
This statistic, which is most often heard in conjunction with those from the studies of psychologist Albert Mehrabian, gives importance to the nonverbal cues on which communication focuses.
Benefits of Verbal Communication in the Workplace
- Improve clarity: Employees can use verbal communication to present their views and instructions in an appropriate manner, avoiding confusion. Unlike written communication where some questions are left unanswered until sufficient information is available.
- Faster decision-making: With verbal communication in the office environment, information is shared and absorbed more quickly, speeding up the decision-making process for teams. Discussions, meetings, and brainstorming allow for instant exchange of ideas and feedback, reducing the duration of various projects and enhancing collaboration across teams. This is especially valuable when real estate teams are comparing CRM platforms in meetings, such as evaluating DealMachine vs PropStream.
- Better team collaboration: By enhancing verbal communication, which is vital for effective teamwork, employees feel comfortable expressing their opinions and are more likely to share their ideas openly. This environment of comfort and transparency not only fosters innovative solutions but also strengthens team unity, ultimately improving productivity across the organization.
- Conflict resolution: In any organization, improving collaboration across teams is important in resolving verbal conflicts and misunderstandings. With direct interaction, issues can be resolved immediately, reducing the likelihood of such serious effects as regret in a work environment.
- Improved leadership: Through verbal communication, leaders are able to motivate and influence followers to achieve a particular vision. To be an effective leader, one must be able to communicate verbally with others and physically to explain or persuade changes so that the team perceives the organization in the desired way. This is why business leadership training often emphasizes honing communication skills, as they are fundamental for inspiring teams and fostering a shared vision.
Understanding what is a cyberattack — a deliberate attempt to compromise or disrupt digital systems—has become increasingly important in written communications, especially for safeguarding sensitive data shared through professional channels.
Types of Verbal Communication
There are several types of oral communication, depending on the context and the number of people involved. Each type serves a different purpose and requires different communication skills.
Intrapersonal
Intrapersonal communication is the communication carried out by a person using only mental processes (with oneself). It includes self-talk, inner talk, self-examination and cognition. Developed intrapersonal communication works out ways of self-understanding that in turn develop cognition and emotion management. Recognizing signs can also provide deeper insight into one’s thoughts, emotions, and personal growth. For example, when a student has to make a presentation, he or she may rehearse his or her speech from within, criticize his or her own argument, and prepare for the presentation through intrapersonal communication. Every person uses intrapersonal communication to think about certain issues or emotional states, a construction that allows us to interact with others in a more efficient manner. Participating in language immersion programs can further strengthen intrapersonal communication by encouraging individuals to think and process ideas in a new language, enhancing cognitive flexibility and self-expression. This guidance helps students manage challenging tasks effectively and gain more confidence in their academic performance.
Interpersonal
Interpersonal communication refers to the way people communicate effectively with each other and includes the exchange of information, ideas, and feelings. It is one of the most widely used means of communication and includes face-to-face conversations, telephone conversations, and dialogues. It is an important process that takes place throughout the day to establish and maintain both social and professional relationships. Some aspects of interpersonal communication, such as listening, showing understanding, and speaking, determine how people interact, how disagreements are resolved, and how people work together.
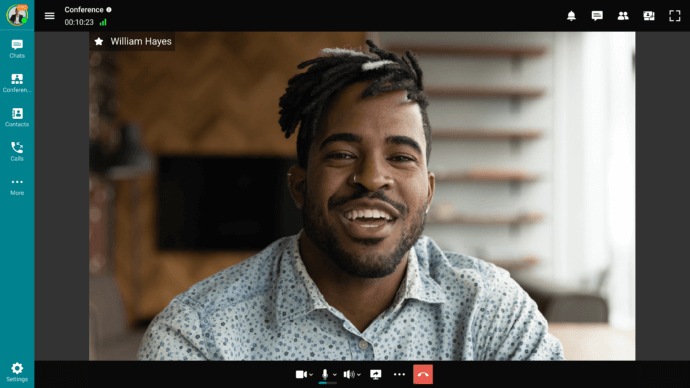
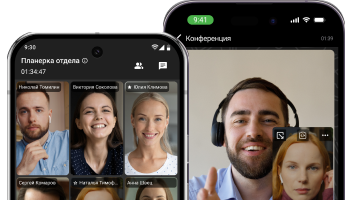
An example of interpersonal verbal communication with TrueConf
Group
Group communication involves at least three people talking or exchanging ideas with a common agenda in meetings or a collaborative task. This type of business communication is necessary in situations where people need to work together and reach a common conclusion. Group communication allows different points of view to be expressed, thus encouraging originality and new ideas. In digital meetings, factors like VoIP latency can affect how smoothly these ideas are exchanged. It involves the ability to speak up, contribute appropriately, express ideas with clarity, and pay attention to everyone in the group and the interactions among group members.
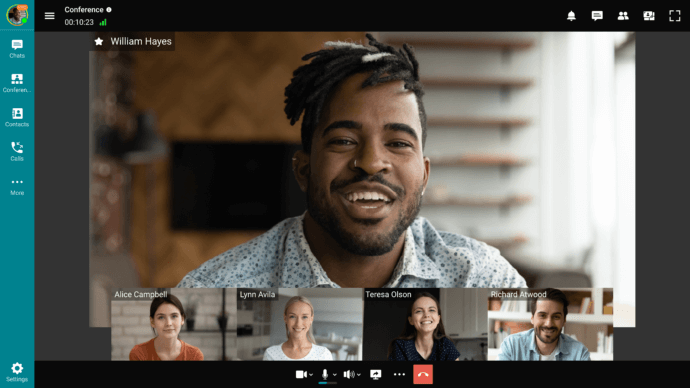
An example of group verbal communication with TrueConf
Public
Public discourse can be seen as an individual addressing a crowd, as in a speech, presentation, or lecture. This type of communication is usually organized in a particular way where there is a goal, whether it is to inform, instruct, or entertain the audience. Skills related to public speaking are essential in many cultures, both business and social, including education and politics, where clear and authoritative delivery of a message can change perspectives and stimulate action. For those looking to enhance these abilities, investing in learning based on skills can be highly effective, focusing on improving key areas like confidence, clarity, and audience engagement.
Mass
Mass communication is the process of disseminating information to large audiences through technologies such as television, radio, newspapers, and the Internet. Unlike interpersonal and group communication, mass communication is relatively free from direct feedback from the audience, making it difficult to assess the immediate impact of a message. Mass communication is most often used for commercial, news or social purposes. It can be used to capture leads during the sales process, inform the public or persuade them to take a particular action
Basic Verbal Communication Skills and Tips to Improve Them
1. Clarity and Conciseness:
Use the most appropriate and least technical language that will help convey the message quickly and without misunderstanding.
Pro tip: Take a few seconds to outline what you want or intend to say in your speech. Say only what you need to say and do not include unnecessary information that may make the audience uncomfortable.
2. Mind Your Tone:
Practice delivering messages in your speech the way you want to sound. You can also record yourself or even practice in front of a mirror where you can see your tone and expressions in relation to the words you are saying.
Pro tip: Seek the opinions of people you trust about your delivery style, as people often refer to it. Your intention then is to address these specific issues and make corrections, such as speaking softly in stressful situations when the topic being addressed is very sensitive, or trying to motivate someone by speaking loudly. You will find that this becomes more and more common with practice, as you develop more and more awareness of yourself and your audience, and more and more of an instinct for what sound is needed.
3. Seek Feedback:
Seek feedback on your communication style from anyone who can help, such as colleagues, friends, or mentors. Use digital booklets to gather quick feedback in a more engaging way. Others’ opinions can help you see things you may not have noticed and help you make adjustments.
Pro tip: Always consider feedback when asking for or looking at things you want to work on, such as clarity, tone, level of engagement. It is also important to remember that feedback is helpful, not negative, so be positive about any feedback you receive. Do the things that need to be done and come back to evaluate how things have changed.
4. Engage in Public Speaking:
Participate in public speaking events such as attending meetings, giving presentations, or joining a public speaking club. These experiences will help you develop confidence, articulation, and audience engagement.
Pro tip: Start with quick, low-stakes opportunities like team meetings or one-on-one presentations to colleagues if public speaking seems daunting. Meanwhile, focus on perfecting your performance in these relatively more relaxed settings before attempting to speak in front of larger crowds.
5. Slow Down and Think Before You Speak:
It is also very important to think before you start speaking so that your speech is smooth and flowing and there are no stray words like “um” or “like”. Also, give your audience a chance to catch up.
Pro tip: In discussions, it is good practice to wait a few moments after hearing a question before trying to formulate an answer or jumping right to the point. Waiting in this situation will help you put your ideas into good grammatical sentences by using appropriate vocabulary to enhance the contribution, especially when supported by tools like the AI answer that can refine clarity and structure.
Conclusion
Verbal communication is a fundamental aspect of human interaction, shaping the quality of our relationships and the outcomes of our endeavors. By honing our verbal communication skills, we can enrich our personal and professional lives, fostering deeper connections and achieving greater success. Embracing the art of effective expression through spoken words empowers individuals to convey their thoughts and emotions with impact and authenticity, ultimately enriching the fabric of human communication.
FAQ
What is verbal communication?
Verbal communication is the exchange of information using spoken words. It includes face-to-face conversations, phone calls, video meetings, and presentations. Tone, clarity, and pace strongly influence how the message is understood.
Why is verbal communication important in the workplace?
It helps teams share ideas, align on goals, and resolve issues quickly. This reflects the importance of corporate training, since training programs often focus on improving speaking and listening skills. Strong verbal communication builds trust and strengthens professional relationships.
What are the key elements of effective verbal communication?
Clarity, active listening, appropriate tone, and concise messaging are essential. Speakers should structure their thoughts logically and adapt their language to the audience. Feedback ensures the message is understood correctly and prevents misunderstandings.
How can someone improve their verbal communication skills?
Practice speaking clearly and confidently in different settings. Focus on active listening and avoid interrupting others. Instead of searching for thesis writing help or asking someone to write my assignment for me, developing real communication skills through practice leads to long-term improvement.
What are common barriers to verbal communication?
Language differences, unclear wording, and emotional tension can distort messages. Poor listening skills and distractions also reduce effectiveness. Personal beliefs, including interpretations of spiritual signs and meanings, may further influence how tone and intent are perceived.
About the Author
Olga Afonina is a technology writer and industry expert specializing in video conferencing solutions and collaboration software. At TrueConf, she focuses on exploring the latest trends in collaboration technologies and providing businesses with practical insights into effective workplace communication. Drawing on her background in content development and industry research, Olga writes articles and reviews that help readers better understand the benefits of enterprise-grade communication.




Follow us on social networks