What is Hybrid Learning? A Complete Guide for 2026
Hybrid learning is a sophisticated combination of both in-person and online learning. This model combines traditional in-class experience and the use of multimedia materials shared online. Students can access materials like lectures, readings, and discussion boards at any time, making it possible to learn at their own pace. Hybrid learning can be especially useful for students who need more time to process information or for those who want to get more out of their in-person class sessions.
The virtual elements of the hybrid learning should be complementary to the in-person ones. The advantages of this way of learning can include closer interaction between peers, greater involvement in educational courses, a more flexible schedule, and an interactive learning experience.
How Hybrid Learning Differs from Traditional Learning?
Unlike traditional learning, which requires all students to be physically present, hybrid learning allows for flexibility in how, when, and where education is delivered. This model supports both synchronous (real-time) and asynchronous (on-demand) learning, making it ideal for today’s diverse and dynamic learning needs. For example, a working professional can continue their education through hybrid learning without interrupting their job, allowing them to gain new skills that can build their resume.
|
Feature |
Traditional Learning |
Hybrid Learning |
|---|---|---|
|
Location |
Physical classroom only |
Mix of physical and online environments |
|
Flexibility |
Fixed schedule and place |
Learn anytime, anywhere |
|
Technology Use |
Minimal (projector, whiteboard, etc.) |
High (video conferencing, LMS, digital tools) |
|
Student Engagement |
Face-to-face only |
Both in-person and online interaction |
|
Learning Pace |
Same for all students |
Can be personalized and self-paced |
|
Access to Materials |
In-class handouts, textbooks |
Digital content available 24/7 |
|
Assessment Methods |
Mainly in-person tests |
Mix of online quizzes, assignments, live exams |
|
Resilience to Disruption |
Low (e.g., during pandemics) |
High – learning can continue remotely |
|
Teacher Role |
Central knowledge source |
Facilitator and guide |
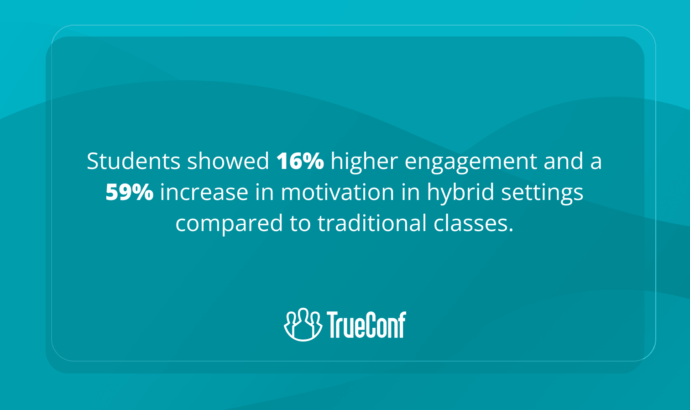
What are the Benefits of Hybrid Learning?
Flexible education and convenience
For students unable to attend physical classes, hybrid learning allows remote study, enabling them to recorde lectures, and online discussions. Hybrid learning ensures that education can happen anytime, anywhere, catering to students with geographical constraints. Because of its flexibility that has increased the number of home-schooled students up to 4.3 million.
Time and cost savings
Hybrid learning can significantly ease the burden of traveling to physical campuses, with both financial and time benefits. Students can save significantly by avoiding costs associated with daily or weekly transportation, such as fuel costs, parking fees, and public transportation. In addition, time spent traveling can be refocused on more productive pursuits, including additional study, work, or personal activities. You can even use a receipt tool to provide cost savings for your students when they do their taxes. For example, freelancers can take money off their education costs (proven via a payment receipt) if it has anything to do with their business.
Effective resource management
Hybrid learning optimizes teaching resources. Teachers can divide students into smaller groups, allowing better space management and accommodating more students in smaller classes. EdTech tools streamline the creation of course materials, reducing teachers’ workload.
Personalized learning paths and enhanced engagement
Hybrid learning allows for a more personalized learning experience. Students can study remotely at their own pace, revisit challenging concepts, or explore additional resources online. While in-person interactions foster community and collaborative learning, online components with multimedia elements cater to diverse learning styles, ensuring better engagement. Learning analytics can help educators monitor progress and address gaps quickly, whether expert English tutors or GCSE Physics tutors guide the lessons. Adaptive exercises and interactive content further support student understanding. This approach encourages self-directed learning while maintaining structured guidance. It also allows teachers to focus on areas where students need the most support, maximizing overall learning outcomes.
Utilization of modern tools
Most hybrid models use Learning Management Systems (LMS), e-learning software, or online course platforms that can significantly enhance the learning experience, offering more streamlined and efficient management of educational resources. These platforms help educators organize content, track progress, and facilitate discussions.
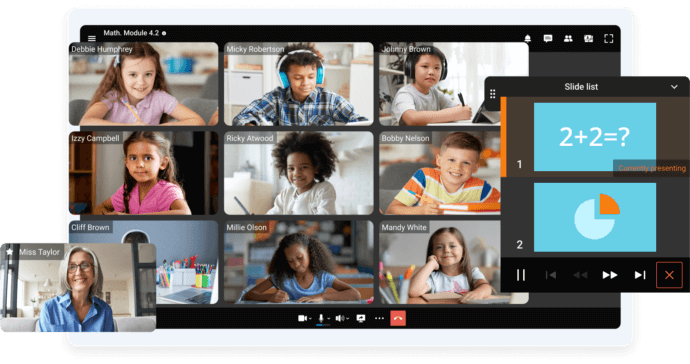
Preparation for the future
Hybrid learning prepares students for modern workplaces by incorporating the use of digital tools like QR codes, email attachments, feedback surveys, and text-to-speech, which enhances their ability to quickly access and share information, fosters engagement with interactive learning materials, and cultivates adaptability in navigating technology-rich environments.
Challenges of Hybrid Learning
While hybrid learning offers flexibility and broader access to education, it also introduces several challenges that institutions must address to ensure effective delivery and equitable experiences for all learners.
Technology Requirements
As hybrid learning heavily relies on digital infrastructure, applying PAM best practices for privileged access management can further secure platforms and protect sensitive systems from unauthorized use helping institutions maintain secure and efficient hybrid learning environments. Both students and educators need access to stable internet connections, compatible devices, and education software that support video conferencing, file sharing, and real-time collaboration. In areas with limited digital access, this can create a significant barrier to participation and inclusivity.
How to Fix?
- Provide device loan programs or subsidies for students in need.
- Ensure compatibility with mobile devices and low-bandwidth modes.
- Offer technical support and training for students and staff.
- Use lightweight, browser-based tools that don’t require installation.
Teacher Workload and Training
Educators often face a steeper learning curve when transitioning to hybrid formats. Preparing materials suitable for both in-person and online learners requires additional time, effort, and technical knowledge. Many remote students prefer to learn in smaller lessons, which means teachers must rethink content delivery and break it into digestible segments. Without proper training and support, teachers may struggle to manage dual audiences and maintain instructional quality across both formats.
How to Fix?
- Provide dedicated time and compensation for hybrid lesson planning.
- Offer regular professional development workshops.
- Share lesson templates, digital tools, and teaching best practices.
- Create peer support networks among educators for shared resources.
Student Disconnection or Isolation
Students learning remotely may experience feelings of isolation, disengagement, or reduced motivation—especially if they lack regular interaction with peers or instructors. Without intentional strategies for inclusion and engagement, hybrid models risk leaving remote learners behind socially and academically.
How to Fix?
- Schedule regular check-ins with online students via video or chat.
- Promote group work that mixes remote and in-person participants.
- Use interactive tools like polls, chat, and breakout rooms.
- Design assignments that value both online and classroom contributions equally.
Coordination and Communication Issues
Managing a class split between physical and virtual participants can lead to miscommunication, uneven participation, and logistical challenges. Coordinating schedules, assignments, and feedback across platforms requires streamlined systems and clear communication protocols to prevent confusion and ensure all students stay on track.
How to Fix?
- Centralize communication through a single LMS or platform.
- Set clear expectations for both online and offline students.
- Synchronize class schedules, deadlines, and calendars.
- Record sessions and provide recaps to ensure no one is left behind.
Hybrid Learning vs. Other Models
Hybrid vs. Online Learning
Online learning is fully remote, with all content, interactions, and assessments conducted through digital platforms. It typically allows for more asynchronous learning, enabling students to progress at their own pace.
Hybrid learning, by contrast, combines in-person and online sessions. Students are expected to participate in both modalities according to a set schedule, making it more structured and time-bound than fully online programs.
Key Difference: Online learning is 100% virtual, while hybrid includes mandatory face-to-face components.
Hybrid vs. Blended Learning
Blended learning integrates online materials and tools into a traditional classroom setting but doesn’t always separate the audience into remote and in-person learners. All students are physically present most of the time, with technology enhancing lessons and helping schools manage and preserve assets such as learning materials and infrastructure more efficiently.
Hybrid learning, on the other hand, actively splits instruction between in-person and remote environments. Some students may be in the classroom while others join from home.
Key Difference: Blended enhances in-class learning with tech; hybrid splits delivery between online and in-person participants.
Hybrid vs. HyFlex Learning
HyFlex (Hybrid-Flexible) learning gives students full control over how they participate—either in person, online synchronously, or asynchronously. Students can switch modalities week by week, depending on their preference or situation.
Hybrid learning offers less flexibility, typically assigning students to in-person or remote groups for a set period.
Key Difference: HyFlex maximizes learner choice; hybrid follows a more fixed structure.
Summary Table: Comparison of Learning Models
|
Feature/Model |
Online Learning |
Blended Learning |
Hybrid Learning |
HyFlex Learning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Location |
Fully remote |
Mostly in-person |
Mix of online & in-person |
Flexible (student decides) |
|
Schedule Flexibility |
High (often async) |
Medium |
Medium (fixed sessions) |
Very high |
|
In-Person Component |
None |
Frequent |
Regular (but split) |
Optional |
|
Technology Use |
Essential |
Supplemental |
Essential |
Essential |
|
Student Choice |
Limited |
Limited |
Medium |
High |
How to Set Up Hybrid Learning?
1. Define Learning Goals and Delivery Model
Start by identifying which courses or subjects are best suited for hybrid delivery. Consider the learning objectives and decide which components should be conducted in person and which can be moved online. Some educational courses may benefit from real-time interaction, while others work well asynchronously. Clarifying the structure early on helps educators and students understand expectations and learning pathways.
2.Choose the Right Technology Stack
Selecting the right combination of platforms is critical to hybrid success. Institutions need reliable video conferencing for education tools for live sessions and a learning management system (LMS) to distribute materials and track progress. Collaboration features such as shared documents, virtual whiteboards, and discussion forums also play a key role in keeping students engaged. It’s important to ensure all tools are accessible on various devices and functional under different internet conditions.

3. Prepare the Physical and Digital Classroom
Classrooms must be equipped with the appropriate audio-visual technology to support two-way communication between remote and on-site students. This includes cameras, microphones, and displays that allow everyone to see and hear each other clearly. On the digital side, teachers should organize learning materials in one central hub where students can find lesson plans, assignments, published ebooks and digital textbooks, and lesson recordings, and even access to dedicated platforms managing fire system maintenance for safety compliance. A consistent structure helps reduce confusion and keeps everyone on the same page.
4. Train and Support Educators
Teachers transitioning to hybrid learning need time, training, and support. Beyond learning to use new tools, they must adapt their teaching methods to engage two different audiences simultaneously. Providing regular workshops, peer mentoring, and technical support empowers educators to grow comfortable in the hybrid classroom. Over time, their confidence and creativity will improve the overall quality of instruction.
5. Engage and Support Students
Students must also be prepared for the shift in learning style. Clear onboarding, video tutorials, and regular guidance can help them navigate both the technology and the academic expectations. Educators should check in frequently with online learners to address issues of motivation or isolation. Creating opportunities for collaboration between remote and in-person students fosters a sense of community and shared purpose.
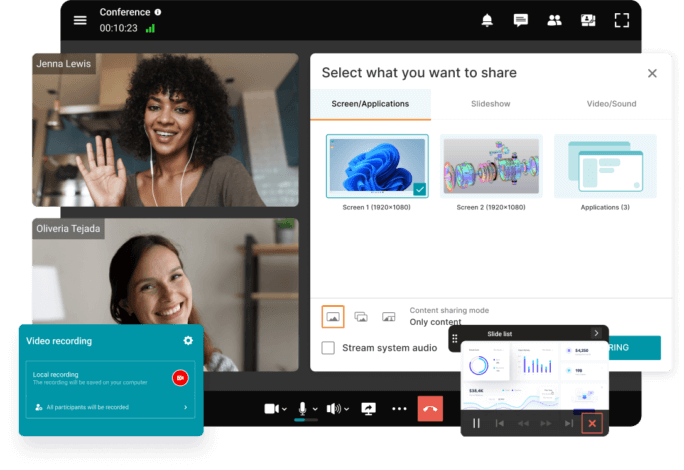
6. Establish Policies and Communication Protocols
Clear rules and consistent communication are essential in hybrid learning environments. Institutions should define policies around attendance, participation, grading, and online conduct. Communication channels—whether through LMS announcements, emails, or messaging apps—should be used regularly to keep everyone informed. When protocols are predictable and transparent, it’s easier to maintain engagement and trust.
7. Monitor, Evaluate, and Improve
Hybrid learning is not a set-it-and-forget-it model. Regular feedback from students and teachers should guide ongoing improvements to content, technology, and teaching practices. Data from LMS platform can help identify participation gaps or performance issues. Treating hybrid learning as an evolving process ensures it continues to meet the needs of both educators and learners.
Real-World Examples of Hybrid Learning
|
School or University Use |
Corporate Training |
|---|---|
|
A university offers a history course where half of the students attend lectures in person, while the other half join remotely via a secure video conferencing platform. Lectures are streamed live, recorded for later viewing, and accompanied by digital materials uploaded to the learning management system. Students participate in discussions through live chat, contribute to shared documents, and complete assessments online. Instructors hold virtual office hours to ensure remote learners remain supported and engaged. This model allows for social distancing, accommodates international or commuting students, and ensures that everyone receives the same quality of education regardless of location. |
A multinational company launches a new product and needs to train sales teams across several regions. The core training session is delivered live from headquarters and broadcast to both onsite staff and remote employees through a unified communications platform. Participants access pre-training materials through an internal portal and complete knowledge checks online. Trainers facilitate breakout sessions for group work, while managers host follow-up Q&A meetings in person or over video. This hybrid setup reduces travel costs, accelerates training rollout, and ensures a consistent learning experience for employees in different time zones and locations. |
The Future of Hybrid Learning
Rather than being a temporary solution, hybrid learning is becoming a long-term strategy for inclusivity, resilience, and modernization. As we move forward, several technological and pedagogical trends are shaping what hybrid education will look like in the coming years.
Trends Shaping Hybrid Education in 2026+
Flexible, Cloud-Based Learning
Institutions are moving to cloud platforms that enable real-time, remote access to lessons, resources, and collaboration tools.
Personalized, Modular Education
Learning is becoming more self-paced and skill-focused through microlearning, modular content, and competency-based assessments — a trend also reflected in how technical fields like Python software development services approach training and upskilling.
Technology-Driven Engagement
Tools like AI, AR/VR, and analytics are enhancing interactivity, adapting content to individual needs, and creating immersive hybrid learning experiences.
Role of AI, AR/VR, and Personalization
Artificial intelligence is playing a growing role in customizing learning experiences—adapting content, pacing, and support based on individual student performance. AI chatbots are increasingly used to provide instant feedback, answer student questions, and offer guidance, enhancing the sense of support in both remote and in-person settings. Virtual and augmented reality are being used to simulate real-world environments for immersive training in fields like healthcare, engineering, and the arts. These tools enable students, whether on-site or remote, to engage in interactive, hands-on learning that was previously possible only in physical settings. Together with data analytics and intelligent tutoring systems, AI and XR technologies are creating hyper-personalized hybrid experiences that are more engaging, accessible, and effective than traditional models. A virtual campus tour further extends these possibilities by allowing students to explore institutions remotely in an immersive way.
Power Your Hybrid Learning with TrueConf!
A powerful self-hosted video conferencing solution for up to 1,000 users, available on desktop, mobile, and room systems. Seamlessly connect in-class and remote students through HD video, share presentations, assignments, and whiteboards in real time, switch from classroom chat to live lessons instantly and use AI-driven tools for smarter collaboration and engagement.
Final thoughts
Hybrid learning is a completely new way to provide education in ever-changing post-pandemic circumstances, when self-isolation and strict lockdown limitations can literally save lives. Hybrid learning eliminates barriers and makes education accessible to any person with a smartphone or a PC and internet connection. For schools, universities and private teachers it is really important to explore infinite opportunities that video conferencing technology can bring and provide innovative learning experiences to pupils and students, no matter where they are and what platform they are using.
For an all-in-one consistent hybrid learning experience, you can try TrueConf! TrueConf offers integrated virtual classroom space with a special mode that brings full focus to the teacher. With TrueConf, you can run unlimited meetings with up to 1,500 participants, organize webinars and even stream your classes to YouTube, while our APIs and SDKs allow for quick integration with any LMS.



Follow us on social networks