Configuration of KVM hypervisor on Linux Using Ubuntu as Example
TrueConf Server can be deployed on a virtual machine (VM). However, this is a very complex task and we do not recommend this procedure to inexperienced users: correct configuration of a virtual machine may sometimes be very difficult.
This guide will describe the configuration of the KVM hypervisor (Kernel-based Virtual Machine). We will take the example of the server running on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS. However, the instructions provided below may be helpful if any Linux distribution is used since KVM is a part of the kernel.
Below we will show how to use KVM with the help of the terminal and on Linux with a graphical shell.
Updating packages
Before starting, update packages by running the command:
|
1 |
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y |
How to check if KVM is supported
The KVM module is a hardware-based virtualization tool based on Intel VT or AMD SVM; so, this method cannot be used on CPUs that do not support this technology.
Run this command in the terminal to check if hardware-based virtualization is supported:
|
1 |
egrep -c '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo |
In this case the program displays 4. If the result displayed by the program is larger than 0, hardware-based virtualization is supported. Here, the result is equal to 4.
KVM configuration
KVM installation
Run this command to install the packages needed for virtualization:
|
1 |
sudo apt install -y qemu-kvm virt-manager libvirt-daemon-system virtinst libvirt-clients bridge-utils |
If you are using Linux that supports the graphical shell, you can also install the virt-manager utility which will provide you with a graphic user interface (GUI) for managing virtual machines.
|
1 |
sudo apt install -y virt-manager |
After installing KVM, you can start its configuration.
How to enable virtualization
Run the Libvirt service with these commands:
|
1 2 |
sudo systemctl enable --now libvirtd sudo systemctl start libvirtd |
After launching the service, restart the computer and check the status of the Libvirt service by running the command:
|
1 |
sudo systemctl status libvirtd |
Adding a user to KVM and Libvirt groups
To make sure that the OS account you are using was allowed to create and manage virtual machines, this account should be added to KVM and Libvirt groups. For this purpose, execute these commands:
|
1 |
sudo usermod -aG kvm,libvirt $USER |
Creation of a network bridge
If you are intending to access the virtual machine from outside the network, then it is necessary to create a network bridge for this machine.
We will show how one can connect to a virtual machine via an Ethernet port of the host. Let us suppose that the port is connected to the router that distributes IPv4 addresses via DHCP and the VM will receive an IP address in the same way. Please note that the configuration of the yaml file on your PC may differ from the example below. So, we recommend checking the documentation.
- Get the list of network interfaces in the host OS:
- Select the required interface, for example,
enp1s0. - In the directory /etc/netplan create the file 01-netcfg.yaml with the following text:
--name [virtual machine name]— the virtual machine name;--vcpu [number of allocated threads]— allocation of CPU threads;--memory [amount of allocated RAM in MB]— allocation of RAM, size in MB;--network [network interface]— the type of network interface;--boot [boot device priority]— the order of boot devices for the virtual machine, boot devices;--disk [virtual disk location, size in GB]— virtual disk emulation, location, size in GB;--cdrom [path to CD-ROM]— CD-ROM emulation, path to its contents.- Select the way of installing the operating system, for example, from an ISO image:
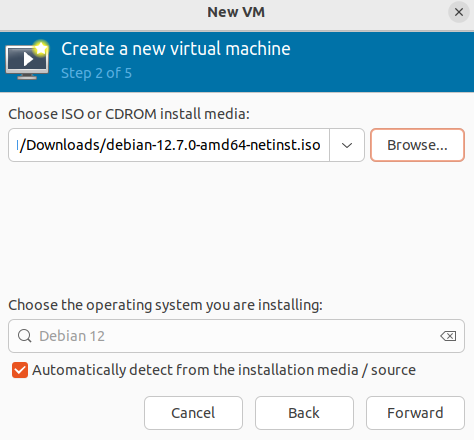
- Select the file of the operating system image:
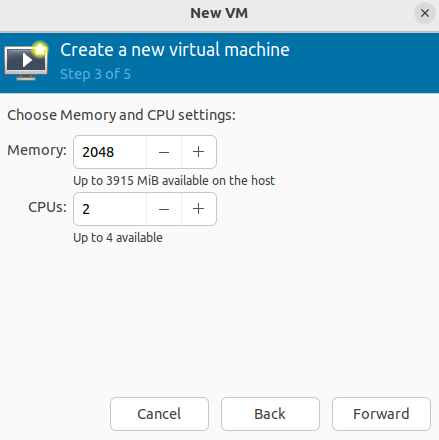
- Specify the required size of RAM and the number of virtual cores (vCPUs) for the VM:
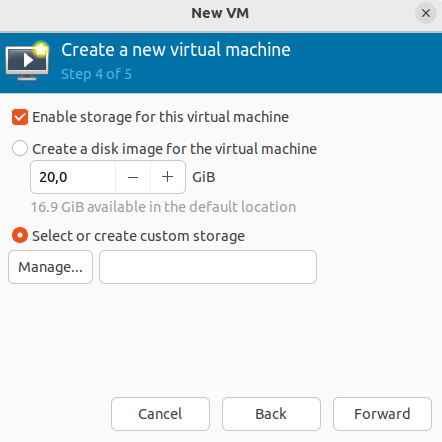
- Configure data storage space. Please note that if you select the option Create a disk image for this virtual machine, the disk will be created in the root directory. To create a storage in the required directory select the option Select or create custom settings and click Manage.
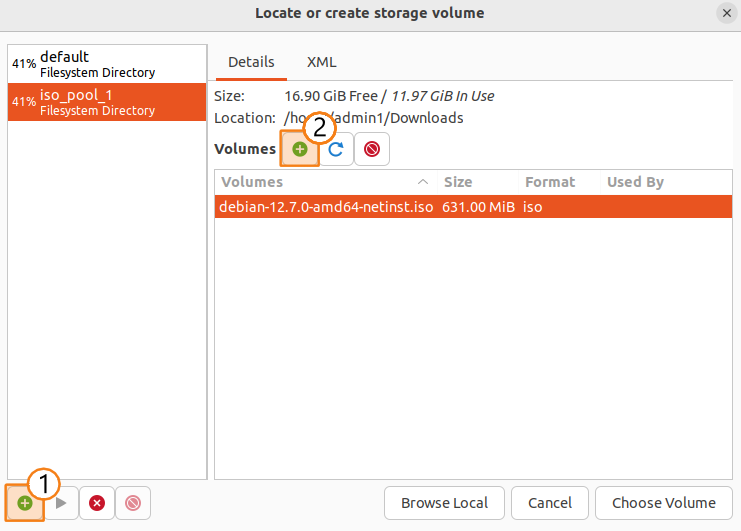
- Create a data pool and add a volume in this pool for the virtual machine:
- Add a pool by following instructions in the manager.
- Add a volume by following instructions in the manager.
- Test the configuration of the virtual machine. It is important to select the correct network. In this case, we are referring to the network bridge br0 created with the help of the yaml file.
- We have made sure that hardware-based virtualization is supported;
- The network bridge for the virtual machine has been created;
- The virtual machine has been configured.
|
1 |
ip a |
For example, the following result is displayed:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: enp1s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether c0:3e:ba:28:f6:93 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 10.140.1.108/22 brd 10.140.3.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp1s0 valid_lft 28101sec preferred_lft 28101sec inet6 fe80::dc33:1ae7:97d0:524a/64 scope link noprefixroute valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
network: version: 2 renderer: NetworkManager ethernets: enp1s0: dhcp4: true dhcp6: true bridges: br0: interfaces: [enp1s0] dhcp4: true dhcp6: true |
To create a file with the help of the terminal, you may use this command:
|
1 |
nano /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml |
To apply changes, execute the command:
|
1 |
sudo netplan apply |
After applying changes, run the following command to check if the network bridge has been added:
|
1 |
ip add show |
Make sure that the network interface br0 is included in the list.
Working with virtual machines
How to create a virtual machine with the help of the terminal
To create a virtual machine, run this command:
|
1 |
virt-install --name [virtual machine name] --vcpu [number of allocated threads] --memory [amount of allocated RAM in MB] --network [network interface] --boot [boot device priority] --disk [virtual disk location, size in GB] --cdrom [path to CD-ROM] |
где:
Example of a full command:
|
1 |
virt-install --name vmtest1 --vcpu 2 --memory 2048 --network bridge=br0 --boot cdrom,hd,menu=on --disk path=/media/admin/Files/kvmt1/vmtom1,size=30 --cdrom /media/admin/Files/downloads/debian-12.5.0-amd64-DVD-1.iso |
To check if the virtual machine has been created, execute the command:
|
1 |
virsh list --all |
The list of all virtual machines will be displayed in the terminal:
|
1 2 3 |
Id Name State -------------------------- - vmtest1 shut off |
Creating a virtual machine in a manager with GUI
Find the manager of virtual machines in the list applications and run it:
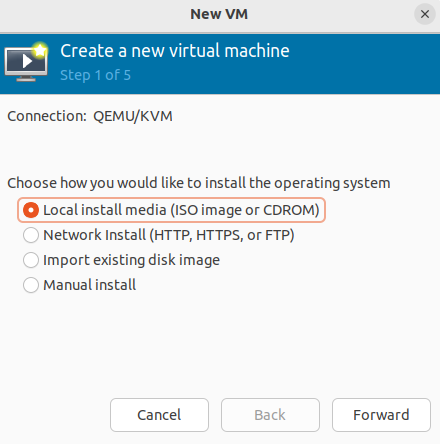
To create a virtual machine, click on File → Create a virtual machine and take the following steps:
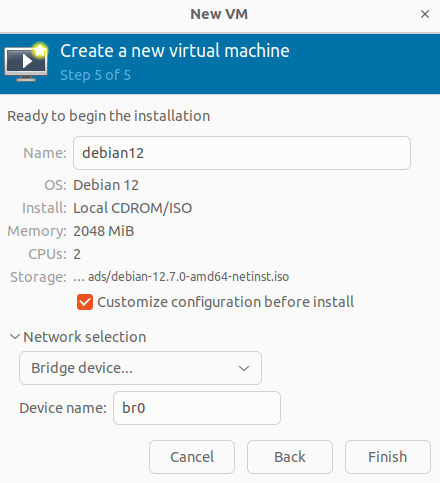
When the test is complete, click Finish. A pop-up window will open; here you can view the configuration of the virtual machine.
After testing the current configuration, click Start installation.
Launch of the virtual machine
As a next step, run the virtual machine and install the operating system (in our case Debian 12) on it.
Using a virtual machine with the help of the terminal
To launch the virtual machine, run the command:
|
1 |
virsh start [virtual machine name] |
To check if the machine is running, execute the command:
|
1 2 3 |
Id Name State ------------------------- 14 vmtest1 running |
To display the virtual machine, run the command:
|
1 |
virt-viewer [virtual machine name] |
Using a GUI manager to control the virtual machine
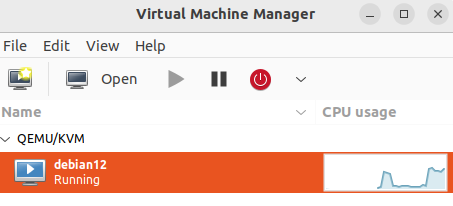
To run the VM in the manager window, right-click on the configured virtual machine and select the Start option.
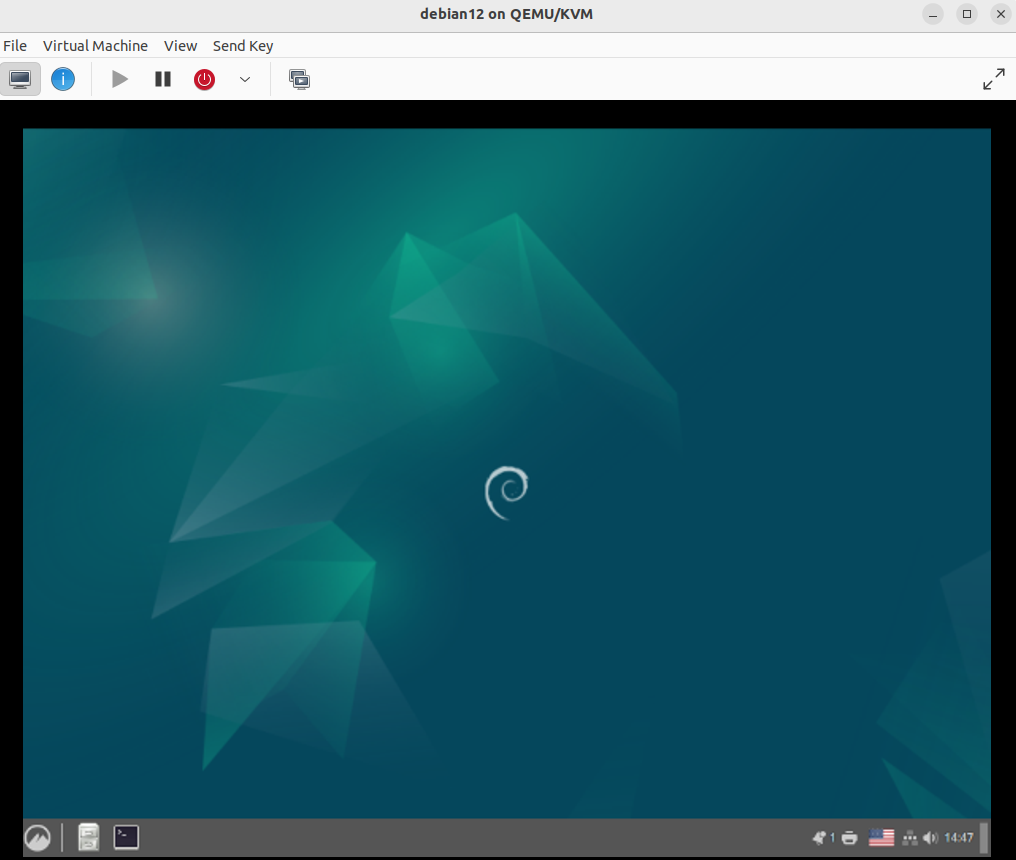
Install the OS, by following the instructions in the VM window.
TrueConf Server installation
Now everything is ready for the installation of TrueConf Server on the virtual machine, in particular:
Install TrueConf Server as it is shown in our guide. After installation, you can add user accounts, configure HTTPS and other TrueConf Server parameters. If you have any questions, please contact our technical support.
Other Resources: