Noise Suppression
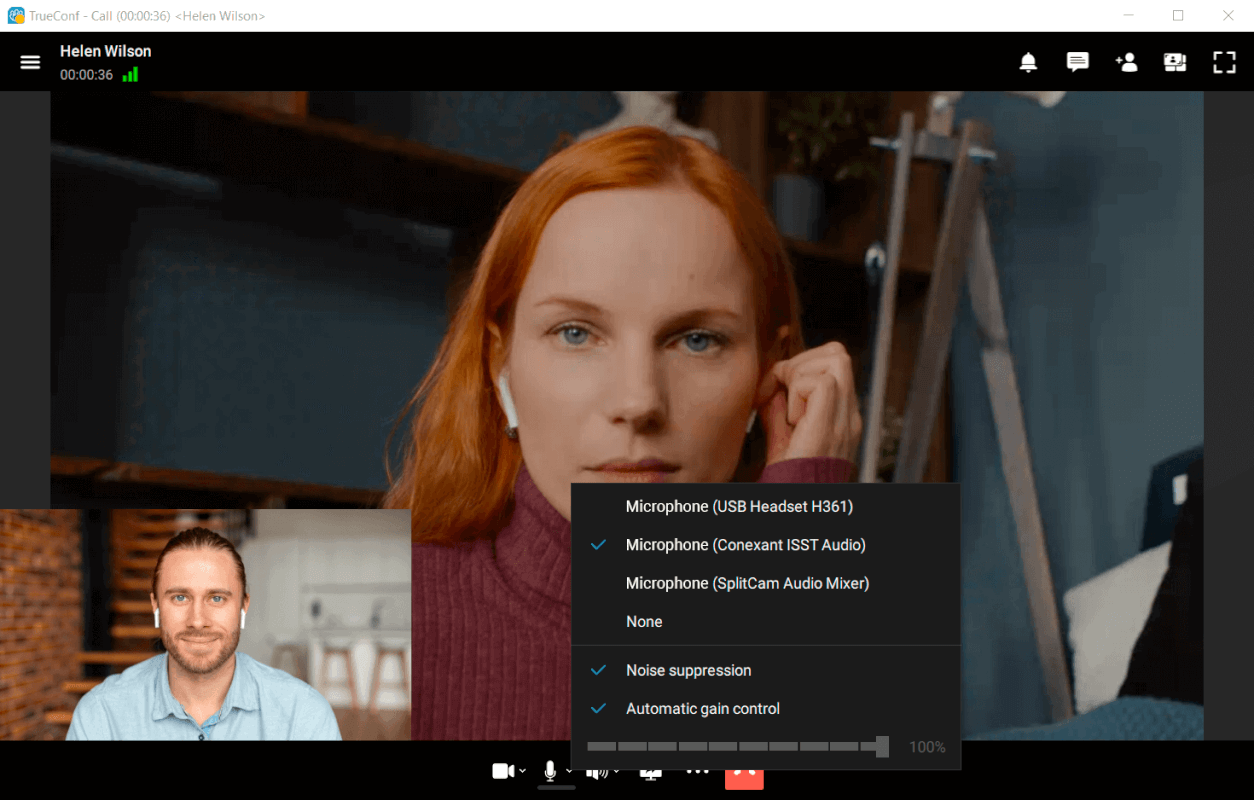
Noise suppression is the process of eliminating or reducing the level of background noise in desired signals in order to improve the audio quality. Clear sound is very important in video conferencing. Sometimes this clarity can be disrupted because of the distortion and background noises. There are two levels of distortion: high and low.
Low distortions differ from high ones in that they are more “gentle”. Whereas high level of distortion is characterized by severe interference, prolonged and intrusive noise, and significant changes to the voice signal. The most common disturbances include clicks, wheezing, rumbling, whistling, humming, and buzzing.
To mitigate these issues, acoustic products can be highly effective in absorbing and diffusing sound, creating a quieter environment that enhances clarity and communication. By installing acoustic panels in your workspace, you can significantly reduce noise and improve overall audio quality for more productive meetings.
Noise Classification
Noise can be constant and periodic (pulsating). Constant noise is divided into tonal and broadband types. The basic features of tonal noise are buzzing and humming.
The main difference between tonal and broadband noise is that the latter has a frequency coloring, but it has no distinct frequency band. Broadband noise is characterized by sounds like a whistle and roar. It is necessary to use noise suppression systems in order to eliminate unwanted noise.
The main objective of noise suppression is to eliminate and/or reduce noise during a video conference. Most methods of noise suppression affect the quality of the transmitted sound, but thankfully, modern algorithms are able to modify the audio stream in a way that minor changes are not noticeable to the human ear.
Noise Сancellation Systems
Noise reduction systems are designed for equalize the signal-to-noise ratio (the ratio of the noise level to the signal). They are used for processing audio and video signals. There are two types of noise reduction systems: filtering systems, which involve remove noise from the desired signal, and systems that convert the signal for transmission across noisy channels.
Noise suppression systems, unlike noise reduction systems, completely turn off low-frequency amplifiers in the absence of the desired signal. There are spectral (disabling the audio amplifier) and amplitude noise cancellers (detect the ratio between the desired signal and noise).
Today, many manufacturers of equipment for video conferencing are ready to provide their users with devices that combine several useful features. For example, a speakerphones with built-in echo cancellation and noise reduction. These devices are capable of delivering a high level of audio comfort even in large rooms.

Follow us on social networks