Unified Communications and Collaboration Solutions: Features, Benefits & Use Cases
Unified Communications and Collaboration (UC&C) represents a strategic integration of calling, messaging, video conferencing, and teamwork functionalities within a singular interconnected ecosystem, and modern unified communications and collaboration solutions bring these capabilities together in one connected platform. When communication tools remain siloed — voice services isolated from chat applications, meetings disconnected from file sharing — organizations suffer contextual fragmentation, inflated operational expenses, and IT management complexities.
This comprehensive resource deciphers UC&C and UCaaS frameworks, details essential platform capabilities, examines prevalent deployment strategies, and provides actionable guidance for selecting an optimal business solution.
What is Unified Communications and Collaboration (UC&C)?
Unified Communications and Collaboration (UC&C) constitutes an integrated suite of communication and teamwork technologies enabling seamless employee connectivity regardless of location. Rather than navigating disconnected applications, users engage with core communication channels through a unified interface, typically featuring synchronized contacts, real-time presence indicators, and embedded connections to critical business applications.
The mission is straightforward: accelerate communication velocity, enhance collaborative fluidity, standardize customer engagements, and empower IT teams with centralized oversight for security protocols, user governance, and policy enforcement.
UC&C Definition in Plain English
UC&C harmonizes everyday tools — voice communications, team messaging, video conferencing, document collaboration, and workflow automation — into an interconnected continuum where interactions flow organically between channels. A practical illustration: initiating a video conference directly from a chat thread with a single click, or having a customer support call automatically surface relevant CRM records without manual intervention.
What UC&C Typically Includes
Leading UC&C platforms deliver a standardized capability set engineered to unify daily communication channels and collaborative workflows into a cohesive experience. Though vendors present features through unique packaging, fundamental building blocks remain consistent, mastery of these elements enables accurate assessment of a solution’s ability to replace fragmented point solutions without functionality gaps.
Business Calling (VoIP/PBX Features)
Comprehensive UC&C deployments incorporate cloud-based or on-premises VoIP systems with PBX-level functionality for internal/external communications. This includes local/toll-free number assignment, custom extensions, intelligent call routing (time-based, skill-matched, queue-driven, or availability-triggered), alongside auto-attendants/IVR systems, hunt groups, and inbound call queues.
User-centric features encompass voice messaging with transcription services, call forwarding/transfer options, shared line appearances, ring groups, and compliance-focused call recording with configurable retention policies and access permissions. These capabilities operate uniformly across desk phones, softphone applications, mobile interfaces, and conference room systems under a unified identity framework.
Video Meetings
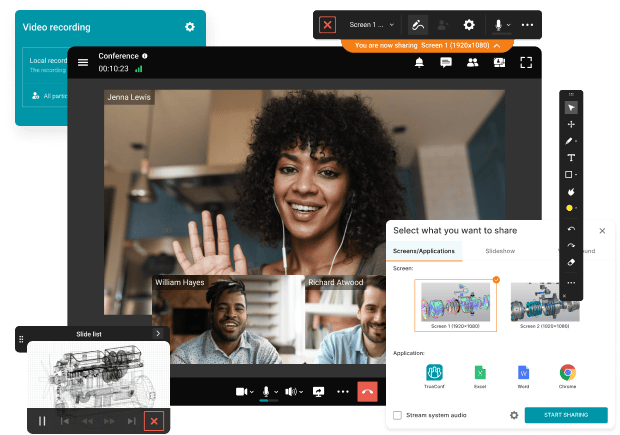
Modern video conferencing facilitates both scheduled and spontaneous collaboration, featuring native calendar integrations (Outlook or Google) for meeting links, recurring session management, and participant coordination. Users can escalate chats or contact interactions to video meetings instantly.
Foundational functionalities include screen or content sharing, in-meeting messaging, presenter management tools, interactive reactions, and moderation controls. Advanced implementations support large-scale webinars or events (with registration portals, role assignments, Q&A moderation, and analytics), enterprise-grade governance policies (recording permissions, external participant controls), and compatibility with specialized conference room hardware including controllers, PTZ cameras, and integrated speakerphone systems.
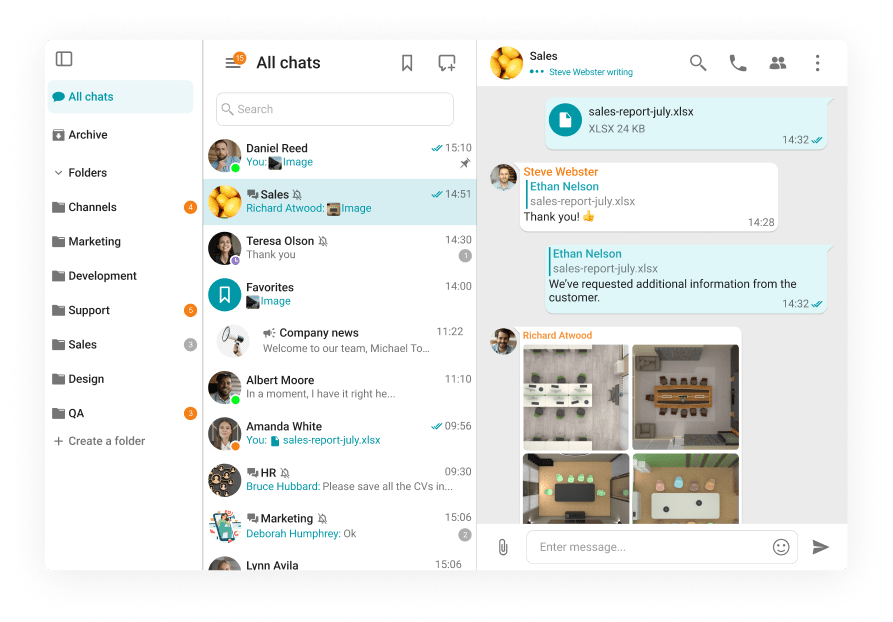
Team Messaging
UC&C messaging environments support 1:1 conversations, group discussions, and persistent topic-based channels or spaces functioning as workflow command centers. These spaces naturally incorporate file attachments, contextual @mentions, content previews, and real-time notifications from integrated applications (CRM updates, ticketing system alerts). A defining strength is fully searchable message history preserving decisions and contextual threads, reinforced by retention schedules, eDiscovery protocols, and granular permission frameworks ensuring regulatory compliance in sensitive operational environments.
Presence and Status
Presence indicators synchronize real-time availability status (Available, Busy, In Meeting, Away, Do Not Disturb) across all user devices and calendar systems, enabling colleagues to determine optimal contact methods. Advanced implementations maintain consistent presence visibility across calling and meeting interfaces, support customizable statuses (“Focus Mode,” “Client Meeting”), and implement intelligent DND rules that permit priority contacts to bypass interruptions while maintaining workflow continuity.
Contacts and Directories
UC&C platforms typically feature centralized organizational directories reflecting team structures, departmental hierarchies, and role-based permissions. This enables intelligent call routing logic, targeted group messaging, automated room booking, and accelerated collaboration discovery. Enterprises frequently synchronize these directories with identity management systems (Azure AD, Okta, Google Workspace) to automate user lifecycle processes, reduce administrative overhead, and strengthen security through consistent access governance.
Collaboration Features
Beyond core communications, sophisticated UC&C platforms embed collaborative functionalities including contextual file sharing across chats and meetings, real-time co-authoring via productivity suite integrations, and native digital whiteboards for brainstorming sessions. Some solutions extend into workflow automation — task assignments, approval workflows, reminder systems, and process triggers — making this layer a critical differentiator.
Vendors diverge philosophically: some pursue all-in-one workspace strategies while others emphasize deep integration with existing productivity ecosystems.
Integrations
Integrations transform UC&C platforms into operational workflow engines by connecting communication streams to CRM databases, helpdesk systems, and project management tools. This enables powerful use cases: displaying customer histories during live calls, auto-logging interaction details, and pushing ticket or project updates directly into relevant team channels.
Implementation occurs through native connectors, application marketplaces, or custom API development. Integration depth frequently determines a solution’s true value, as it directly impacts the reduction of disruptive context-switching across applications.
Why Do You Need a Unified Communications Solution?
Organizations adopt UC&C not as a technological trend but as a direct response to daily friction within disconnected communication environments. When calling systems, meeting platforms, and chat applications operate in isolation — further complicated by separate contact center solutions, file repositories, and task managers — teams expend excessive energy on context switching rather than productive work.
UC&C resolves this by establishing a consistent communication and collaboration layer, enabling users to initiate conversations through appropriate channels, escalate interactions seamlessly when required, and maintain complete contextual visibility for all stakeholders.
Key drivers propelling UC&C adoption include:
Communications Are Fragmented Across Too Many Tools
Disparate applications scatter critical context: decisions vanish into private chats, meeting conclusions remain undocumented, and customer data resides separately from conversation records. This fragmentation forces repetitive explanations, constant app-switching, and operational delays.
UC&C consolidates chat histories, call logs, meeting recordings, file repositories, and decision trails into a unified searchable environment, ensuring work remains transparent, traceable, and easily resumable.
Teams Need Faster Escalation and Less Context Switching
Natural conversation progression, from initial chat to voice call to video meeting, becomes cumbersome in fragmented systems. Users manually share meeting links, re-invite participants, and re-explain contexts during transitions, dissipating momentum and scattering action items across disconnected tools.
UC&C enables fluid escalation paths (message → voice call → video session) while preserving the original thread and context. Teams resume discussions in shared spaces with outcomes and next steps permanently visible and searchable.
Remote and Hybrid Work Require Consistent Experience
Modern distributed teams require uniform communication experiences across office, home, and mobile environments. Mismatched toolsets create uneven access — features missing on mobile devices, unreliable notification systems, inaccessible conversation histories — resulting in duplicated messages and redundant meetings.
UC&C delivers consistent desktop, mobile or web experiences with unified identity and presence synchronization, enabling seamless collaboration continuity across locations and time zones without dependency on office-centric infrastructure.
IT Needs Centralized Management, Security, and Compliance
Each additional communication tool multiplies administrative complexity: separate management consoles, inconsistent security policies, fragmented audit logs, and configuration vulnerabilities. This complicates access governance and sensitive data tracking.
UC&C centralizes user provisioning, permission management, data retention policies, and activity monitoring within a single platform. Integration with SSO or MFA frameworks and identity providers enhances lifecycle control, while unified analytics and quality-of-service monitoring streamline performance troubleshooting and system reliability.
Customer-Facing Teams Need Better Routing and Responsiveness
Unstructured inbound communication channels lead to missed interactions, delayed transfers, and poor agent availability visibility. Customers suffer repeated explanations during handoffs: a problem magnified across multiple channels, regions, and departmental boundaries.
UC&C enhances responsiveness through intelligent call routing, queue management, auto-attendant systems, and presence-based availability indicators. CRM and helpdesk integrations inject customer context during interactions, while analytics transform service quality into measurable, improvable workflows.
Unified Communications and Collaboration Benefits
UC&C advantages manifest as measurable business outcomes rather than feature checklists. Unified platforms fundamentally reshape daily interactions: conversations accelerate, contextual continuity strengthens, and cross-departmental collaboration becomes reliably consistent.
Instead of treating communication channels as isolated functions, UC&C weaves them into an integrated workflow mirroring natural human collaboration patterns. Organizations typically experience simultaneous improvements across three dimensions:
- Operational efficiency: Reduced friction and redundant efforts
- Workforce effectiveness: Accelerated decision cycles and cohesive teamwork
- Customer experience: Enhanced responsiveness and reliable service transitions
Over time, these enhancements simplify communication management and scalability, particularly vital for globally distributed enterprises.
Productivity
UC&C eliminates productivity drains through consolidated logins, minimized application switching, and reduced time spent locating messages or documents. By integrating chat, calling, meetings, and file sharing into a unified workflow, teams instantly escalate interactions (message → call → meeting) while maintaining searchable context and outcomes within persistent shared spaces.
Improve Flexibility and Responsiveness
UC&C delivers consistent identity and interface experiences across desktop clients, mobile applications, desk phones, and conference rooms, supported by presence indicators that guide optimal contact timing. Cloud or hybrid deployment models ensure uniform collaboration capabilities and intelligent routing logic across geographical regions and time zones, accelerating organizational responsiveness without contextual loss.
Reduce Costs
Savings emerge from consolidating overlapping meeting, chat, and telephony tools onto a standardized platform, eliminating license redundancies and vendor management overhead. UCaaS models further reduce capital expenses by transferring infrastructure maintenance, upgrades, and high-availability management to providers.
Significant “hidden” savings arise from decreased IT workload, fewer systems requiring patching, reduced integration maintenance burdens, and diminished support tickets stemming from fragmented toolsets.
Improve Customer Satisfaction
UC&C improves customer experiences through context-rich interactions enabled by intelligent routing, seamless handoffs (including warm transfers), and rapid internal collaboration. CRM and ticketing integrations empower agents to access complete customer histories and pending actions during live interactions while automatically logging activities.
This minimizes repetitive explanations, prevents dropped requests, and transforms service quality into consistent, measurable outcomes.
Facilitate Collaboration
Persistent channels, shared interaction histories, and in-context file sharing create always-accessible workspaces supporting asynchronous teamwork across time zones. Decisions remain discoverable post-meeting within contextual threads.
Teams can dynamically involve stakeholders, share materials, escalate to live sessions when necessary, and preserve outcomes visibly afterward, all while ensuring remote participants maintain equal access to communication histories and decision rationales.
Unified Communications and Collaboration Examples (Use Cases)
While industry-specific applications vary, UC&C consistently aims to interconnect calling, messaging, meetings, and collaboration workflows to accelerate execution with minimized handoffs and preserved context. Maximum value emerges when UC&C evolves beyond tool deployment into standardized workflows linking personnel, processes, and business systems.
Business
In business environments, UC&C bridges CRM-driven sales processes (one-click calling, instant escalation to product demos, shared meeting notes or recordings) with internal coordination through persistent project channels, scheduled check-ins, and searchable decision archives. This minimizes inter-departmental friction and enables effortless transitions from asynchronous discussions to real-time collaborative sessions without conversation restarts.
Education
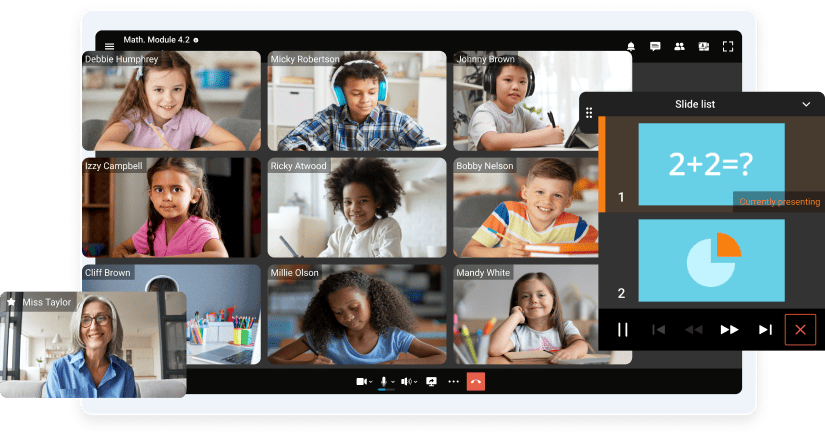
Academic settings leverage UC&C for remote or hybrid learning via scheduled class sessions, screen sharing capabilities, participant moderation tools, and accessibility features ensuring consistent pedagogical experiences across physical and virtual classrooms. The platform additionally supports student tutoring and faculty office hours through rapid scheduling tools and spontaneous chat-initiated consultations. Centralized administration consoles streamline staff communications and secure large-scale messaging operations.
Healthcare
Medical organizations implement UC&C for telehealth appointments, clinical case consultations, and cross-specialty coordination where system reliability, data privacy, and rapid response are non-negotiable. The technology also secures internal staff communications and operational workflows like on-call scheduling and emergency escalation protocols.
UCaaS Solutions Overview
UCaaS (Unified Communications as a Service) delivers UC&C capabilities through subscription-based cloud or hybrid models, reducing infrastructure management burdens while enhancing scalability. Understanding underlying architecture and ecosystem connections is essential for evaluating solution reliability, security robustness, integration depth, and long-term organizational fit.
Architecture and Core Components
Contemporary UCaaS platforms integrate desktop/mobile/web clients (frequently extending to dedicated meeting room systems) with centralized cloud or hybrid communication layers managing identity frameworks, messaging infrastructure, meeting services, and administrative policy enforcement. Telephony services typically operate via SIP trunking with PSTN connectivity through carrier partnerships or gateway/SBC configurations.
These systems feature synchronized directories linked to corporate identity providers, augmented by governance capabilities including call/meeting recording archives, retention policy engines, audit logging systems, and analytics dashboards for diagnosing performance across diverse networks and endpoints.
Integrations and Ecosystem
UCaaS platforms transcend communication tools to become workflow orchestration hubs through strategic integrations:
- Productivity suites for calendar synchronization and document collaboration (Microsoft 365/Google Workspace)
- CRM systems enabling click-to-dial functions and automatic activity logging (Salesforce/HubSpot)
- Service management tools linking conversation threads to support tickets (Zendesk/Jira)
- Identity platforms providing SSO, MFA enforcement, and automated user lifecycle management (Azure AD/Okta)
Custom workflows leverage APIs and webhooks to automate alert routing to channels, generate tasks/tickets from interactions, and synchronize communication metadata across enterprise systems.
How to Choose a Unified Communications Solution for Your Business
Selecting an optimal UC&C/UCaaS solution follows a structured five-phase approach: defining business requirements, validating security frameworks, verifying operational reliability, assessing integration/migration pathways, and calculating comprehensive total cost of ownership beyond base licensing fees.
Step 1: Requirements and Use Cases
Begin by cataloging user personas (corporate staff, frontline workers, sales or support teams, executives, external partners) and prioritizing critical workflows (business telephony, internal messaging, video conferencing, webinar hosting, contact center operations, project channels, client communications).
Quantify expected system loads — total users, peak concurrent meetings, average call volumes — and document geographical coverage requirements including local number availability, PSTN connectivity regions, and performance consistency expectations across global locations.
Step 2: Security and Compliance
Scrutinize data protection mechanisms: encryption standards (in transit and at rest), physical data storage locations and residency controls, external access governance (guest permissions, federation policies, file sharing restrictions). Evaluate DLP capabilities, eDiscovery readiness, configurable retention schedules, legal hold functionalities, and comprehensive audit logging for administrative actions.
Verify access control frameworks (role-based permissions, administrative segregation, MFA/SSO support) and confirm alignment with industry-specific regulations (HIPAA, GDPR, FINRA) and regional compliance mandates.
Step 3: Reliability and Call/Meeting Quality
As UC systems become mission-critical infrastructure, rigorously assess SLA commitments, guaranteed uptime percentages, and redundancy architectures (multi-region failover, backup routing paths, PSTN fallback mechanisms). Confirm support for QoS traffic prioritization and availability of diagnostic tools for identifying quality issues (packet loss analysis, jitter measurement, endpoint/network troubleshooting).
For global organizations, conduct real-world performance testing across key regions via pilot programs using actual office, home, and mobile network conditions.
Step 4: Integrations and Migration
Evaluate compatibility with existing technology stacks: identity providers (SSO/MFA implementation, directory synchronization), productivity environments (Microsoft 365/Google Workspace interoperability), and core business systems (CRM, helpdesk, project management tools). For migration planning, confirm number porting timelines and country-specific coverage, assess support for legacy telephony hardware and meeting room systems, and document network prerequisites (SBC configurations, gateway requirements, hybrid connectivity).
Develop a phased rollout strategy incorporating pilot testing, staged deployment waves, comprehensive training programs, and dedicated change management resources to ensure adoption readiness from launch day.
Step 5: Total Cost of Ownership
Calculate comprehensive financial impact beyond per-user subscription fees: feature-specific add-ons (call recording, webinar hosting, contact center modules), telephony expenses (local number rentals, calling plan structures, per-minute usage fees), and hardware investments (conference room systems, professional headsets, gateway appliances). Factor in professional services costs for deployment/migration, ongoing administrative overhead, tiered support contracts, training expenditures, and integration maintenance.
Uncover hidden expenses stemming from solution complexity — excessive add-on dependencies, extensive customization requirements, or limited administrative tooling — and prioritize platforms demonstrating long-term scalability and operational sustainability.
Top 5 UCaaS Providers
TrueConf Server
Ideal for: Organizations mandating self-hosted UC solutions with absolute control over data residency, security configurations, and infrastructure deployment: common in regulated sectors (finance, government), air-gapped networks, or environments with cloud restrictions.
Advantages: Full infrastructure or data sovereignty through on-premises or private-cloud deployment; optimized for isolated networks and rigorous governance frameworks; centralized administration console for enterprise-wide rollouts.
Limitations: Requires dedicated internal IT resources for deployment, version updates, and 24/7 operational support; management simplicity varies significantly based on self-hosting versus private-cloud managed service models.
Core capabilities: High-definition video conferencing and webinar hosting, enterprise messaging, conference moderation tools, centralized administrative controls, interoperability frameworks (typically SIP/H.323 for legacy system integration in complex environments).
Technical profile: Primarily on-premises/private-cloud deployment; customizable integration with enterprise directories and legacy communication systems; designed for environments demanding strict access controls, comprehensive auditing capabilities, and perimeter-based security architectures.
Empower your video conferencing experience with TrueConf!
Microsoft Teams (Microsoft 365)
Ideal for: Organizations deeply embedded in Microsoft 365 ecosystems seeking integrated chat, meetings, and collaboration—particularly where SharePoint or OneDrive document management and Outlook calendaring are central to daily operations.
Advantages: Seamless channel-based collaboration with real-time co-authoring; native integration with Microsoft 365 identity and productivity applications; extensive third-party app marketplace and certified room system hardware ecosystem.
Limitations: PSTN/telephony implementation complexity (multiple carrier options, layered licensing structures, regional feature variations); enterprise-scale administration requires meticulous governance frameworks to prevent configuration sprawl.
Core capabilities: Persistent team channels, meetings/webinars with background effects, screen or content sharing, cloud recording (license-dependent), document co-editing, granular administrative policy controls.
Technical profile: Deep Microsoft 365 ecosystem integration with app marketplace extensions; enterprise-grade security/compliance tooling compatibility; cloud-first architecture with hybrid identity and policy management options.
Zoom Workplace
Ideal for: Teams prioritizing premium meeting experiences and intuitive interfaces with robust hybrid work and conference room support.
Advantages: Industry-leading meeting user experience and audio or video quality; mature Zoom Rooms hardware ecosystem; comprehensive feature set spanning chat, telephony (Zoom Phone), webinars or events based on subscription tiers.
Limitations: Advanced governance controls, telephony features, and analytics often require premium add-ons; feature availability and PSTN connectivity exhibit regional inconsistencies.
Core capabilities: HD video meetings, team messaging spaces, integrated telephony (region-dependent), webinar or event management, room scheduling systems, AI-powered meeting assistants (premium plans).
Technical profile: Standard calendar/productivity integrations; cloud-native deployment; enterprise security features including SSO enforcement, administrative policy templates, and data encryption controls (tier-dependent).
RingCentral
Ideal for: Enterprises seeking cloud telephony (PBX) as their communication foundation, augmented by messaging and meetings, particularly beneficial for distributed organizations with multiple physical locations.
Advantages: Mature telephony feature set (skills-based routing, IVR workflows, call queuing); scalable architecture for multi-site deployments; comprehensive voice administration tools and call analytics.
Limitations: User experience consistency depends on configuration decisions and regional PSTN coverage; complex bundling structures can obscure direct vendor comparisons.
Core capabilities: Cloud PBX/VoIP services, intelligent call routing or queuing, IVR or auto attendant systems, team messaging, video meetings, centralized administrative console with reporting dashboards.
Technical profile: Pre-built connectors for major CRM and productivity platforms; cloud delivery model with enterprise security configurations (SSO integration, policy-based access controls).
Cisco Webex Suite
Ideal for: Large enterprises requiring secure collaboration with robust governance frameworks, high-reliability meetings, and extensive room device ecosystems, frequently in regulated industries or complex global environments.
Advantages: Enterprise-grade security certifications and administrative controls; proven meeting reliability focus; comprehensive support for Cisco room systems and hardware standards.
Limitations: Implementation and management complexity requires dedicated expertise; licensing structures and feature packaging can be challenging to navigate; maximum value realization demands careful architecture planning and governance frameworks.
Core capabilities: Meetings with noise suppression, persistent messaging, telephony integration (region-dependent), webinar hosting, certified room device support, analytics dashboards, centralized policy management.
Technical profile: Broad integration ecosystem via APIs and partner connectors; industry-leading security/compliance certifications; cloud delivery with hybrid deployment options for organizations requiring infrastructure control.
Key Insights
Contemporary UC&C expectations center on controlled communication layers that interconnect personnel, contextual data, and internal systems, without mandating public cloud adoption. For solutions like TrueConf Server, three pivotal trends dominate: the resurgence of secure on-premises or private-cloud collaboration, intensifying governance and interoperability demands in enterprise settings, and the imperative to support hybrid work models while maintaining organizational control over data and operations.
Secure On-Prem and Private-Cloud Collaboration
Organizations increasingly demand modern collaboration capabilities while retaining communications within their security perimeter, driven by regulatory mandates, data sovereignty requirements, or internal policies. This fuels adoption of platforms like TrueConf Server, deployable on-premises or in private clouds, supporting air-gapped or segmented networks, and providing absolute control over data storage locations and traffic routing paths.
Platform evaluation criteria are shifting from “fastest cloud deployment” to “predictable enterprise operations”: centralized administration consoles, granular role-based access controls, comprehensive auditability features, and consistent cross-site scalability for desktop/mobile/web experiences. In these environments, reliability planning — bandwidth allocation, server sizing, redundancy architectures — and proactive operational monitoring become foundational collaboration strategy elements rather than reactive considerations.
Governance, Compliance Controls, and Managed Access
Enterprise UC&C procurement now prioritizes governance capabilities: defining communication permissions between user groups, configuring recording triggers, establishing data retention periods, and implementing auditable action trails. For TrueConf Server implementations, this necessitates strict alignment with internal policies covering authentication protocols, permission hierarchies, meeting security controls, and retention schedules, particularly critical in organizations requiring administrative separation of duties and forensic traceability.
Optimal practice treats UC&C as an integral security component: mandatory integration with corporate identity providers, rigorous role-based permission frameworks, explicit external participant policies, and standardized recording/retention/audit procedures. This methodology minimizes risk exposure, establishes user behavior predictability, and simplifies compliance audits through centrally enforceable policies.
Interoperability and Infrastructure Readiness
Modern enterprises require UC&C systems to coexist with legacy telephony infrastructure, specialized room systems, and existing network architectures. This elevates interoperability and deployment design to strategic priorities: organizations seek collaboration platforms that integrate with current environments, enable incremental migration paths, and deliver consistent performance across distributed sites.
TrueConf Server deployments typically emphasize network architecture planning (firewall configurations, NAT traversal, bandwidth provisioning), precise server sizing calculations, redundancy implementations, and interoperability validation (especially SIP/H.323 workflows) through controlled pilot programs. The prevailing trend emphasizes operational pragmatism: organizations prioritize solutions demonstrating seamless integration capabilities, enterprise-grade security postures, and predictable large-scale operational performance with clear ownership models.
FAQ
What is the difference between UC and UCaaS?
UC (Unified Communications) defines the conceptual framework and feature set, integrating voice, messaging, meetings, and collaboration capabilities into a cohesive experience. UCaaS (Unified Communications as a Service) specifies the delivery mechanism, provisioning UC capabilities through subscription-based services, predominantly cloud-hosted (though hybrid models exist).
In essence: UC represents the functional outcome, while UCaaS defines the consumption model.
What is an example of Unified Communications?
A tangible UC scenario involves an employee messaging a colleague within a project channel, instantly escalating the discussion to a video conference with one click, sharing their screen to review documents, and continuing the thread post-meeting with shared files and searchable history — all within the same persistent workspace. For customer-facing roles, UC enables CRM click-to-call functionality, intelligent call routing/queuing, and automatic interaction logging to maintain continuous customer context throughout service engagements.
What are the different types of UC solutions?
UC platforms generally align with three architectural approaches:
- Cloud-first UCaaS: Fully managed subscription services (e.g., Zoom, RingCentral)
- On-premises UC: Self-hosted platforms deployed within organizational infrastructure (e.g., TrueConf Server)
- Hybrid UC: Strategic combinations of cloud services and on-premises components for balanced control
Within these models, vendors exhibit distinct “centers of gravity” — some emphasize meeting or collaboration experiences (Teams, Zoom), others prioritize enterprise telephony foundations (RingCentral), while comprehensive suites integrate contact center capabilities (Webex, Microsoft Teams with CCaaS connectors).



Follow us on social networks