What is Cybersecurity? Definition, Importance & Key Concepts
What is Cybersecurity?
Cyber protection, often referred to as IT security, involves safeguarding computers, data servers, portable devices, electronic infrastructures, network systems, and confidential information from digital intrusions or illegal access. This forms an essential part of tech management, which includes anticipating, identifying, and countering cyber risks. These risks can take a variety of forms, such as deceptive phishing, harmful malware, data hijacking ransomware, and disruptive denial of service attacks. Cybersecurity strategies are implemented to preserve the integrity, secrecy, and accessibility of data, making sure that digital systems are functioning at peak capacity. The importance of this sector has grown exponentially as an increasing number of corporations and private individuals store critical information on digital mediums, thus becoming potential victims for cybercriminals.
Human Factor
Considering the realm of cybersecurity, human beings represent the most vital element. This encompasses individuals ranging from IT specialists responsible for maintaining and securing network infrastructures, to each individual who logs into these systems. Usually, humans serve as the initial barrier in cybersecurity. It is imperative for IT experts to keep themselves updated about novel risks and safety measures, while end-users need to understand potential threats and methods of circumventing them. This might involve steps like refraining from opening dubious emails or making sure that information is frequently backed up.
Nevertheless, the human factor can also pose the greatest vulnerability in cybersecurity. Errors committed by humans, such as succumbing to phishing tricks or utilizing weak credentials, can result in substantial security infringements. This emphasizes the necessity for continuous learning and instruction in cybersecurity best practices for everyone employed within a company.
Furthermore, humans aren’t solely participants in the defensive side of cybersecurity. They also take on roles as offenders, like hackers attempting to penetrate systems for nefarious reasons. Comprehending the motives and tactics of these individuals can be pivotal in formulating effective cybersecurity plans. This understanding of both offensive and defensive perspectives has led to collaborative approaches in cybersecurity testing, such as implementing a purple team in cybersecurity that combines red team attack simulations with blue team defensive strategies to create more comprehensive security assessments.
To sum up, humans are crucial to both the robustness and susceptibility of cybersecurity. Their actions and conduct can significantly impact the security of data and systems, highlighting the requirement for thorough and continuous Cybersecurity Certification Training and consciousness.
Processes
In the realm of cybersecurity, “processes” signify the assortment of methods and rules that companies adopt to safeguard their digital systems from prospective security threats. These might encompass measures to pinpoint weak spots, initiatives to obstruct unauthorized entry, and contingency plans for the instance a security violation transpires. Procedures also include periodic checks and modifications to make sure the security protocols remain potent against emerging cyber threats, often using vulnerability scanners to identify weaknesses before they can be exploited. In addition to these procedures, many organizations implement a fraud management system to detect and mitigate fraudulent behavior across digital channels. These systems work in tandem with cybersecurity protocols to monitor transactions, flag anomalies, and respond to suspicious activity in real time—thereby reinforcing the broader defense mechanisms against cybercrime. These are a critical component of a holistic cybersecurity approach, as even the most sophisticated security tech can become ineffectual if the procedures governing its application are deficient or faulty. It is equally crucial that these procedures are transparently conveyed and comprehended by every member of the corporation since human miscalculation can frequently be a vulnerability in cybersecurity fortifications.
Technology
Within the realm of cybersecurity, advanced technology serves as an essential instrument in shielding crucial data and systems from significant cyber risks. Cybersecurity technology is specifically engineered to thwart, identify, and alleviate cyber-attacks. This technology encompasses an extensive assortment of systems including firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, anti-malware software, cryptographic tools, among others. Alongside these systems, dast software plays an important role by scanning and testing web applications in real time to detect potential security flaws by simulating external attacks to uncover vulnerabilities. These cutting-edge technologies are utilized to ensure the preservation of data integrity, secrecy, and accessibility. They assist in safeguarding networks and devices from unauthorized intrusion, data leaks, and additional cyber risks. Incorporating cyber threat intelligence into these systems enhances their ability to anticipate and respond to emerging threats with greater precision and speed.
As technology progresses, the parameters of cybersecurity also broaden. The emergence of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and distributed ledger technologies have ushered in novel aspects to cybersecurity. These advanced technologies are employed to augment the functionality of cybersecurity tools, thereby making them more potent and streamlined. However, these technologies also pose new hurdles and weak points that necessitate attention. As such, keeping abreast with the most recent trends and progress in technology is vital within the cybersecurity sphere.
In summary, technology can be viewed as both a blessing and a curse in relation to cybersecurity. Even though it provides sophisticated tools and strategies to shield digital assets, it simultaneously presents new susceptibilities and threats. Consequently, the objective of cybersecurity is to utilize technology effectively to guarantee optimal security while minimizing potential hazards. For organizations looking to manage digital assets securely and efficiently, consulting a DAM system buyers guide can help select the right platform, ensuring that new technologies are leveraged safely while protecting valuable content.
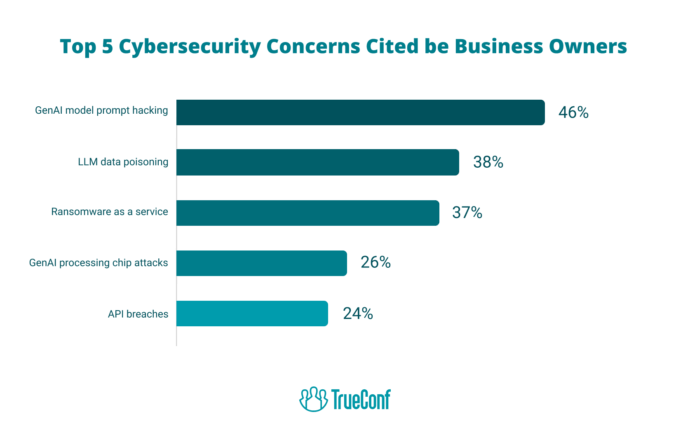
Why is Cybersecurity Important?
Types of Cybersecurity Threats
Various forms of cybersecurity threats exist, each posing distinct challenges for individuals or businesses. One common category encompasses malware, encompassing harmful software such as viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware. These dangerous applications can compromise, encrypt, or erase sensitive information, manipulate critical computer functions, and track computer usage without the user’s knowledge.
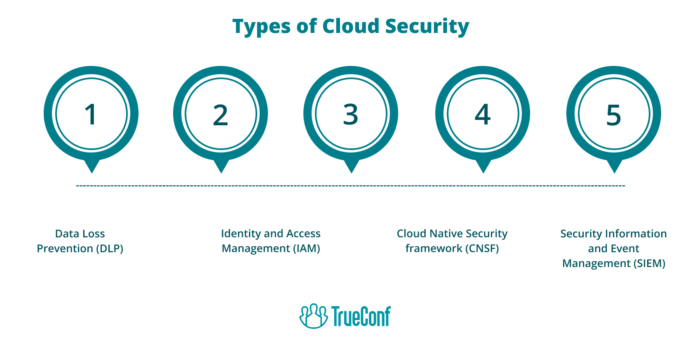
Cloud Security
Falling under the extensive array of cybersecurity dangers, Cloud Security emerges as an important class that requires particular consideration. As an increasing number of companies rapidly transition their functions and data repositories to cloud based services systems, the safety of these systems has escalated to become a critical worry. Cloud security is defined by the guidelines, checks, methods, and technological systems used to safeguard data, software, and the infrastructure connected with cloud computing.
The hazard environment in cloud protection is immense and constantly adapting. Some prevalent risks encompass data infiltrations, data disappearance, account commandeering, threats from within, insecure APIS, and denial of service onslaughts. These dangers can culminate in significant financial deficits, harm to brand image, and erosion of client confidence.
Financial and transactional security is a key part of this. Businesses handling payments must prevent fraud and disputes, and specialized tools, such as this list of chargeback software from SEON, help monitor, manage, and resolve these challenges efficiently, safeguarding transactions and maintaining customer confidence. For businesses exploring custom fintech solutions, security is a key feature they must implement. Any early-stage fintech firms apply for AWS credits through programs like AWS Activate to offset the costs of these high-security environments, allowing them to leverage premium fraud-prevention infrastructure without draining their initial capital.
Consequently, the enactment of sturdy cloud security protocols and data protection services is vital in preserving the wholeness and confidentiality of classified data and averting unauthorised entry or leakage. Organizations leveraging AWS cloud engineering services often benefit from built-in security frameworks and scalable tools that simplify the implementation of robust cloud protection strategies. Professionals in the cybersecurity field frequently utilise a range of instruments and tactics like encryption, access regulation, intrusion alert systems, and security assessment to ensure thorough cloud security.
Identity
The term ‘Identity’ denotes a distinct class of cybersecurity hazards in which digital criminals manipulate the digital persona of individuals or companies. This particular cybersecurity danger frequently employs malicious strategies like phishing, identity thievery, or spoofing. The primary objective remains to trick users into divulging confidential data, enabling the intruder to imitate the victim and secure unauthorized entry to systems and information. Digital criminals have the ability to use purloined identities to execute fraud, execute transactions, disseminate malware, or even initiate targeted assaults against different organizations. The risk to identity highlights the necessity of applying strong authentication and access management protocols in cybersecurity.
Malware
Malicious software, also known as malware, represents a significant cybersecurity risk that includes various detrimental software types like viruses, worms, Trojan horses, ransomware, spyware, and adware. Such malicious software can penetrate and harm devices, pilfer confidential data, and interrupt operations. The distribution of malware typically occurs through email attachments, software downloads, system vulnerabilities, or by visiting compromised websites.
A prevalent form of malware, viruses have the ability to self-replicate and disperse to other files or systems, often leading to widespread damage. Worms bear similarities to viruses but possess the ability to propagate independently, eliminating the need for a host program. Trojan horses present themselves as genuine software but can grant cybercriminals remote access to a device once they’re installed.
Ransomware represents a particularly menacing type of malware that locks a user’s files, demanding a ransom for the restoration of access. Spyware stealthily collects a user’s data without their consent, frequently used for marketing purposes. Lastly, although adware is less damaging, it can be invasive and expose users to additional cybersecurity risks.
The most effective defense against malware involves the use of up-to-date antivirus software, the adoption of secure browsing habits, and avoiding the opening of email attachments received from unfamiliar sources. Regularly backing up critical data can also lessen the impact of a malware attack.
Phishing
Phishing represents a widespread and subtle form of cyber threat. This typically involves employing misleading emails, sites, or text messages to dupe people into disclosing confidential data like passwords, credit card details, or Social Security digits. The culprits disguise themselves as a reliable figure, often mimicking reputable organizations or individuals to gain the unsuspecting victim’s confidence. There exist various forms of phishing attacks, such as spear phishing, where distinct individuals or firms are specifically targeted; and whaling, where top-tier executives become the primary targets. Phishing can lead to substantial financial damages and data leaks, thereby posing a serious risk to both individual users and corporate entities. Therefore, cybersecurity strategies should incorporate strong safeguards against phishing assaults, along with continuous education to assist users in identifying and sidestepping such hazards.

Ransomware
Ransomware remains one of the most commonly seen cybersecurity threats. This particular type of malicious software has been designed specifically to restrict the user’s access to a computer system, unless a certain amount of money, also known as a ‘ransom’, is handed over. Both individual users and large-scale businesses or organizations can become the target of ransomware attacks. The cybercriminal usually gains access to the system via a cleverly disguised phishing scam, which tricks the unsuspecting user into clicking a link that appears harmless, but in reality, downloads the ransomware. Once the malicious software has infiltrated a system, it commences the encryption of files and folders, rendering them useless to the user. Following the encryption, a message pops up demanding a certain payment in order to decrypt and regain access to the blocked files. This payment is typically demanded in a digital currency, such as Bitcoin, in an attempt to maintain the attacker’s anonymity. Fortunately, some systems and services provide flexible payment options, making it easier for victims to respond without adding unnecessary complications. The existence of ransomware presents a severe risk to cybersecurity, as it can result in substantial financial loss and service disruption. Therefore, it is crucial for both individuals and organizations to regularly back up their data and implement stringent security procedures to defend against potential ransomware attacks.
Zero Trust
One particular cybersecurity threat that corporations often confront is the absence of a stringent non-trust policy. The non-trust strategy is a specific safety principle demanding every user, even those within the corporation’s intranet, to undergo authentication, authorization, and ongoing verification of security setup and stance, prior to gaining or retaining access to software and information. This methodology minimizes the risk of an internal threat, a situation that arises when employees inside the corporation misuse their granted access to deliberately or inadvertently breach security. Moreover, it safeguards against outside threats by restricting network access and consistently checking security protocols. In the absence of a non-trust policy, a corporation’s intranet becomes vulnerable to a multitude of cyber threats, such as data leaks and assaults on network assets. Many organizations now adopt specialized zero trust security services in USA to strengthen this model and ensure compliance with modern cybersecurity standards. In the absence of a non-trust policy.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity
Adopting cybersecurity optimal strategies is essential for safeguarding an institution’s information and systems. An essential strategy includes the development of robust password guidelines, involving the creation of intricate passwords, activating dual-factor identification, and consistently modifying passwords. Continual updating and system patching is also crucial to defend against identified vulnerabilities. Patching practices should be tailored depending on the operating system in use, as different systems require specific updates and protocols. For example, organizations can implement a Windows patching solution to automate updates and ensure all Windows devices remain secure. Businesses should also allocate funds for solid security software, such as firewalls, antivirus applications, and intrusion detection systems.
Training staff members is another fundamental component of cybersecurity. Workers must be informed about the dangers of deceptive emails, questionable hyperlinks, and the significance of not disclosing confidential data. Establishing a well-defined policy concerning the utilization of personal gadgets in the workplace can also assist in avoiding security infringements. Employees should also learn how to set up a VPN, implement safe browsing habits, and follow secure file-sharing practices.
Furthermore, businesses should consistently store a copy of their data to avert loss in the event of a digital attack. This preservation should be executed offsite or via cloud storage for increased protection. Regular evaluations of the institution’s cybersecurity protocols can also assist in uncovering any potential vulnerabilities.
Lastly, it’s imperative to establish a contingency response scheme. This scheme ought to detail the measures to be taken following a digital attack, encompassing breach identification, damage containment, threat eradication, and recovery from the onslaught.
Adherence to these optimal strategies enables businesses to significantly enhance their cybersecurity and safeguard against potential hazards.
About the Author
Olga Afonina is a technology writer and industry expert specializing in video conferencing solutions and collaboration software. At TrueConf, she focuses on exploring the latest trends in collaboration technologies and providing businesses with practical insights into effective workplace communication. Drawing on her background in content development and industry research, Olga writes articles and reviews that help readers better understand the benefits of enterprise-grade communication.


Follow us on social networks