Video Conferencing as a Service (VCaaS): A Comprehensive Guide
What is Video Conferencing as a Service (VCaaS)?
Video Conferencing using a Service (VCaaS) functions as an internet-powered approach to delivering virtual meeting tools. Simply described, an external vendor manages the conferencing systems online and provides them to clients using a recurring payment model. As a result, companies can utilize video collaboration tools via the web without deploying specialized equipment or IT systems locally. Through VCaaS, participants can enter video discussions from virtually any place and through nearly any platform – whether it’s a desktop, mobile phone, tablet, or integrated meeting suite – provided they are connected online.
Crucially, VCaaS stands apart from legacy internal setups in terms of its installation and supervision. In a standard in-house environment, a business would purchase and support proprietary video hardware and platforms, running within the organization’s secure infrastructure. This method gives autonomy but demands notable capital expenditure on tools, and expanding usage involves acquiring and integrating more resources. VCaaS, in contrast, runs under a pay-per-use subscription plan, where the vendor oversees the complex backend. This hosted approach enables scalable, real-time access to conferencing services with no requirement for teams to operate hardware or handle performance limits – upgrading often means tweaking a plan, not investing in new systems.
How does VCaaS work?
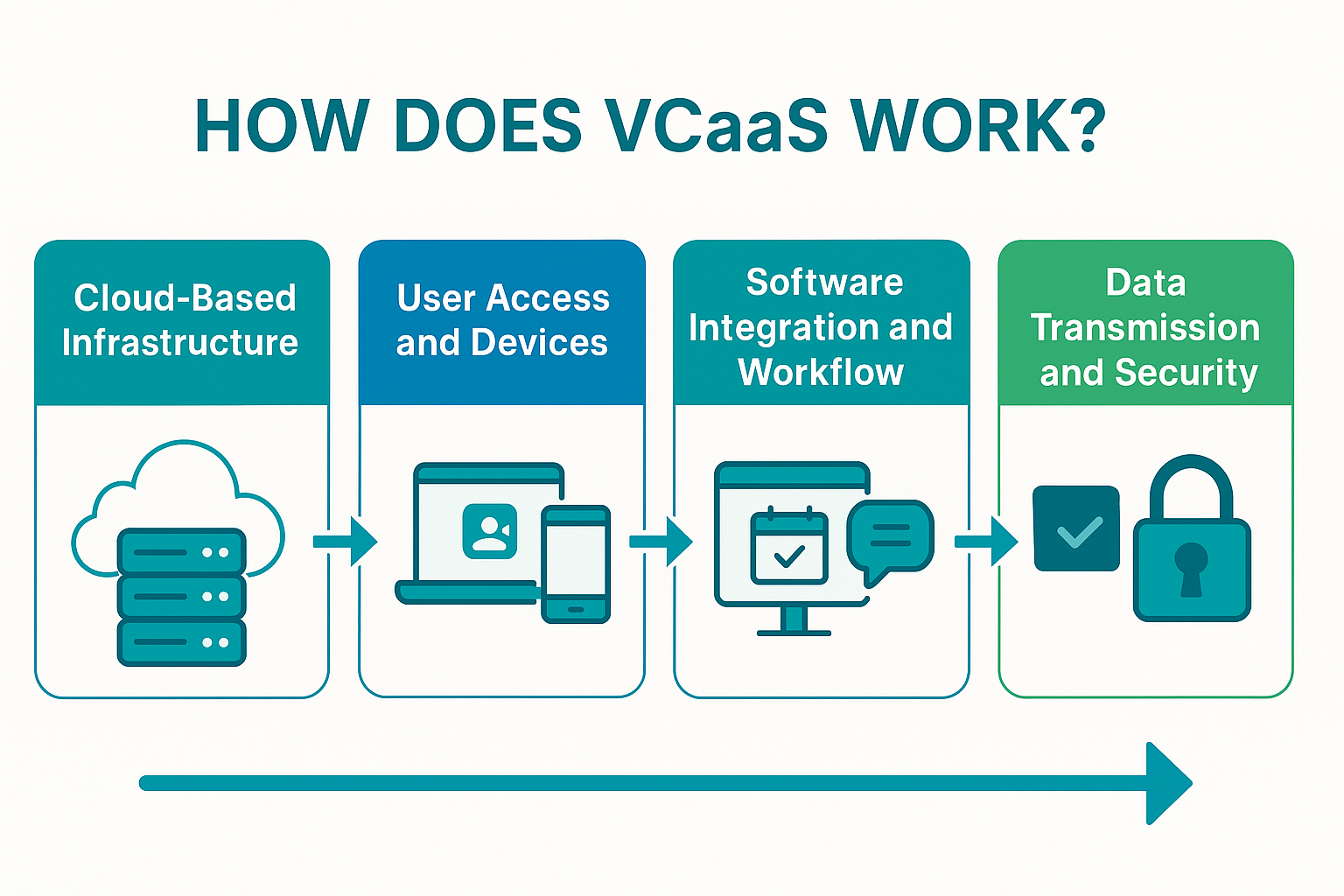
VCaaS utilizes a mixture of digital platforms and technology to offer video conferencing as a flexible, service-based solution. Below is a breakdown of how the system functions:
Cloud-Based Infrastructure
At the heart of VCaaS lies a networked array of data centers (frequently spanning regions) managed by the solution provider. When users arrange or initiate a virtual session via a VCaaS interface, the provider’s distributed systems handle critical operations – including connecting attendees and transmitting media content. This decentralized architecture promotes consistent and scalable service, assigning computing capacity automatically to maintain smooth sessions regardless of user volume. Since these systems run in cloud environments, VCaaS handles server monitoring, reduces interruptions and keeps latency low by selecting optimal server nodes, preserving clarity in both audio and visuals. Providers additionally incorporate fault tolerance and dynamic balancing (via standby nodes, etc.) to eliminate service failure risks, keeping platforms stable even if technical faults occur.
User Access and Devices
Participants normally interact with VCaaS through downloadable software clients or browser-based interfaces. This software communicates across networks with the service provider’s platform. Once admitted into a call, the installed application (whether on a desktop, portable gadget, or room unit) transmits participant audio/video streams to the cloud, which redistributes it live to others. A standout feature is that VCaaS accommodates a diverse array of access methods – from notebooks and phones to tablets and even legacy videoconferencing endpoints like SIP/H.323 systems via compatibility bridges. The platform is built with versatility in mind, allowing entry from whatever device users possess. All that’s required is a connected system with audio/visual input. Such inclusivity means VCaaS supports participants regardless of their work environment – be it office desks, living rooms, or while traveling.
After learning all this about integrating phones and conferencing systems, it’s important to remember that maintaining your hardware is just as essential as configuring your software. Devices used for telephony and conferencing, such as smartphones and tablets, are exposed to daily wear and tear.
Software Integration and Workflow
Today’s VCaaS offerings are frequently embedded within other productivity tools to simplify the end-user journey. They often sync with calendars and messaging tools for single-click session launches or operate alongside corporate systems such as chat suites, scheduling apps, CRM databases, and learning tools. This level of integration lets conferencing slot seamlessly into business routines. Video events can be initiated through apps like Outlook, linked from collaborative dashboards, or connected directly to customer interfaces using embedded APIs – all empowered by the provider’s integration toolkit. Behind the scenes, the vendor supports API access and feature interoperability, enabling companies to deploy conferencing within their ecosystems without hosting internal infrastructure. Secure connections rely on clear API authentication methods, such as token-based access or API keys, to manage data flow between integrated systems.
Data Transmission and Security
Throughout a VCaaS session, voice and video feeds from participants are securely transferred over digital pathways to the provider’s network, then redistributed instantly. This live data flow is a VCaaS cornerstone – providers optimize performance using compression tools and latency-reduction strategies, ensuring responsive and engaging interaction.
Safeguarding these exchanges is vital: top-tier providers use robust encryption (typically end-to-end or at least secured-in-transit using TLS or SRTP protocols) and identity verification to secure communications.
With this delivery model, the vendor oversees all protective measures, continuously updating systems and monitoring for threats, making it essential to know how to choose a web hosting service. Since the infrastructure remains with the provider, enterprise-grade shields like firewalls, DDoS filtering, and compliance layers are part of the package. From a user’s view, joining a session might mean authenticating through secured credentials or access codes, after which the platform encrypts the experience and blocks intrusions. To streamline this login process while maintaining high security, organizations often deploy a robust Dashlane alternative to ensure employees use strong, unique passwords for every session. Ultimately, the background software maintains stability and security, letting participants concentrate solely on collaboration.
Use cases of VCaaS
VCaaS represents a powerful framework and is actively integrated throughout numerous sectors and circumstances. Below are several notable examples where VCaaS proves especially impactful:
Everyday Business Meetings and Remote Work Collaboration:
One of the most widespread applications involves supporting everyday corporate conversations across departments. Teams depend on VCaaS for anything ranging from brief strategy check-ins to external demos and leadership sessions. The technology transforms team interaction, enabling personnel in separate locations (or those working remotely) to engage visually and collaborate on initiatives instantly. For distributed and blended working environments, VCaaS forms a foundational platform – it strengthens internal messaging and reinforces organizational cohesion through frequent face-to-face digital contact. Many firms have observed that task execution becomes quicker and strategic choices more effective when colleagues can launch a fast video call instead of relying on emails alone.
Education and E-Learning:
Institutions such as schools, colleges, and development centers harness VCaaS to facilitate remote instruction and digital education systems. Through these conferencing platforms, instructors can lead interactive sessions or seminars with students connecting from afar, often utilizing tools to present visuals, operate virtual whiteboards, or split participants into smaller group activities. This setup has become essential for remote access to learning and continuing academic engagement. VCaaS helps dissolve geographic constraints, empowering organizations to educate individuals regardless of location. For instance, a college may bring in an international expert to deliver a guest lecture via video, or corporate trainers can conduct global workshops for staff training without needing everyone onsite, and many healthcare teams also support career growth through RN to MSN programs online. Especially when physical classes are restricted (as witnessed during global lockdowns), video conferencing solutions have enabled uninterrupted instruction, pushing education to become more universally available.
Healthcare and Telehealth:
Medical services have swiftly integrated VCaaS into their operations for digital appointments and virtual diagnostics, reducing the burden on call handlers just like emergency dispatch software also does. Through protected conferencing tools, physicians and health workers connect with patients remotely, delivering support to individuals unable to travel due to remoteness, disabilities, or safety guidelines. For example, someone in an isolated region can consult with a specialist from a top hospital without ever leaving home. Similarly, therapists hold sessions online, and healthcare teams conduct case reviews through digital channels. VCaaS empowers clinicians to extend expertise and provide efficient treatment in locations previously underserved. It is also leveraged in medical instruction – surgeries may be broadcast through VCaaS for training other professionals in real time.
The Department of Health of Ho Chi Minh City|Case Study
TrueConf video collaboration solution connected more than 100 hospitals in Ho Chi Minh and allowed converting quarterly medical examination and treatment briefings between the Department of Health and hospitals into online mode. 660 employees of the City Oncology Hospital can now collaborate with one another without any barriers, increasing both speed and efficiency of communications.

Customer Support and Client Engagement:
Businesses increasingly rely on video-based tools to connect with customers as part of assistance and sales initiatives. Support over video can offer a more detailed and empathetic approach than text or voice interactions alone. Support over video can offer a more detailed and empathetic approach than text or voice interactions alone, fostering personalized customer engagement and stronger client relationships. For example, a customer service specialist may switch a technical case to a video walkthrough to guide the user through problem resolution, even seeing shared screens in real time. In sectors like banking and insurance, consultants meet virtually with clients to discuss options for loans or investments. This visual interaction promotes confidence and understanding, especially when combined with advanced contact center software features that streamline call management, reporting, and customer engagement. As companies seek to enhance these capabilities, many explore Freshdesk alternatives — platforms that offer flexible integrations, robust video support, and more tailored customer experience tools to suit specific industry needs.
The direction of support strategies is clearly moving toward more video communication – between 2019 and 2021, adoption jumped from 41% to 57% of firms using video for client service. By 2023, that figure was forecast to reach 65%.
These figures indicate that video conferencing enhances external relationships by enabling more engaging, human experiences that ultimately drive satisfaction and client loyalty.
Virtual Events, Webinars, and Large-Scale Conferences:
VCaaS platforms come equipped with features to host significant online gatherings – from educational webinars to multi-track digital expos. Companies can use these systems for launching new products, running brand campaigns, facilitating expert roundtables, or even organizing global summits entirely online. Attendees participate from across borders, vastly increasing potential audience size. Built-in tools like question management, interactive polls, and on-demand replay allow for rich engagement and post-event content sharing.

Even fields once tied to physical venues – such as trade associations or enterprise marketing – have pivoted toward hybrid or virtual delivery to cut expenses and expand visibility. VCaaS makes this transformation viable by offering stable broadcasting and advanced engagement tools necessary for drawing large virtual crowds.
Future trends in VCaaS
The digital conferencing landscape continues expanding quickly. VCaaS platforms and services are evolving to create virtual interactions that feel more dynamic, contextual, and uninterrupted. Anticipating what lies ahead, a number of significant trends, including the growing role of Machine learning, are expected to influence VCaaS development:
AI-Enhanced Tools and Automation:
Future VCaaS platforms may offer AI-powered live transcription and multilingual translation, enabling automatic subtitles or real-time speech conversion between participants. Smart meeting bots might summarize talking points, assign tasks, or analyze participant tone. Enhanced video algorithms could also upgrade visual or audio streams – for instance, by modifying brightness or refining voice clarity on the fly. Major vendors are also investing in AI scheduling assistants that handle invites, deliver post-call recaps, and manage interactive elements like polls or Q&A.
Immersive AR and VR Meetings:
A growing area of interest is the use of extended reality (XR) in professional communication. Virtual reality, in particular, holds potential to simulate presence and interaction in digital spaces. Soon, VCaaS may support virtual conference environments where participants join through headsets as digital avatars seated around virtual tables. This redefines the sense of proximity using 3D rendering and surround sound, mimicking real-life collaboration. Augmented reality could let attendees overlay complex models or dynamic data into their surroundings using everyday devices. Pioneering examples already demonstrate how remote teams can co-create or present ideas in shared 3D space.
Upgraded Security and Confidentiality:
As virtual discussions become more central to operations (and include confidential subjects), security continues to evolve. More VCaaS providers are embedding end-to-end encryption by default, ensuring that only the intended attendees can access meeting content. New identity safeguards are emerging as well – such as biometric verification for entry or AI-based monitoring to detect and block unauthorized users. Legal compliance will also improve, with features designed to support data control policies, audit procedures, and location-specific storage rules. Stronger protocols will build confidence in platforms, especially as usage expands across sensitive industries. Future tools may even explore blockchain identity tracking or decentralized verification frameworks. While end users may not notice these changes visually, administrators and security teams will gain better visibility – including security analytics, audit trails, and granular permissions. Ultimately, VCaaS providers will offer security by design, aligning with enterprise governance and privacy demands.
About the Author
Nikita Dymenko is a technology writer and business development professional with more than six years of experience in the unified communications industry. Drawing on his background in product management, strategic growth, and business development at TrueConf, Nikita creates insightful articles and reviews about video conferencing platforms, collaboration tools, and enterprise messaging solutions.



Follow us on social networks