How to Control TrueConf Server Using Its API and Telegram Bot
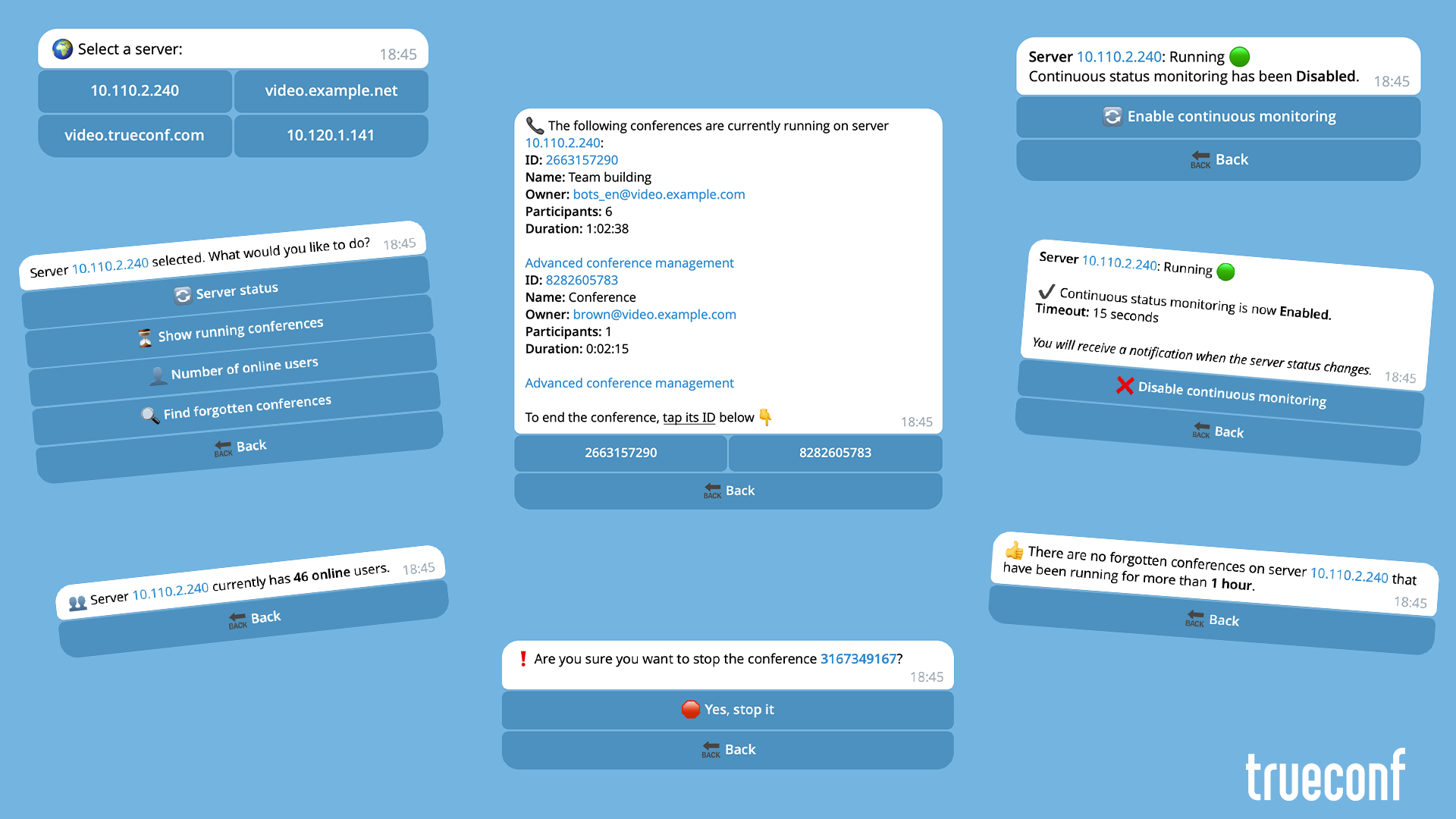
The administrator of TrueConf Server can quickly access important server information using popular messengers, such as Telegram. This can be done by creating a bot that will retrieve the necessary data via the TrueConf Server API. The bot can be hosted locally on your own server or on any dedicated machine.
In this example, we will demonstrate how to create a Telegram bot and deploy it on your local machine. We provide a ready-made example of task implementation using Python:
The proposed bot has the following capabilities:
- Checking server status (running/stopped).
- Retrieving the list of active conferences.
- Checking the number of online users.
- Finding and stopping long-running conferences that were left active by mistake.
In the following text, such mistakenly started conferences are referred to as “forgotten” for brevity, meaning they were not ended by the owner and moderators. For example, during a webinar, the guests left, but the moderator minimized the client application without stopping the event. It continues to run, and if recording was enabled, it unnecessarily occupies space on the SSD or HDD with a growing recording file.
For example, we consider the following conference as “forgotten”:
- it lasts longer than one hour;
- only the owner or moderator remains in it;
- it has participants, but none of them are moderators.
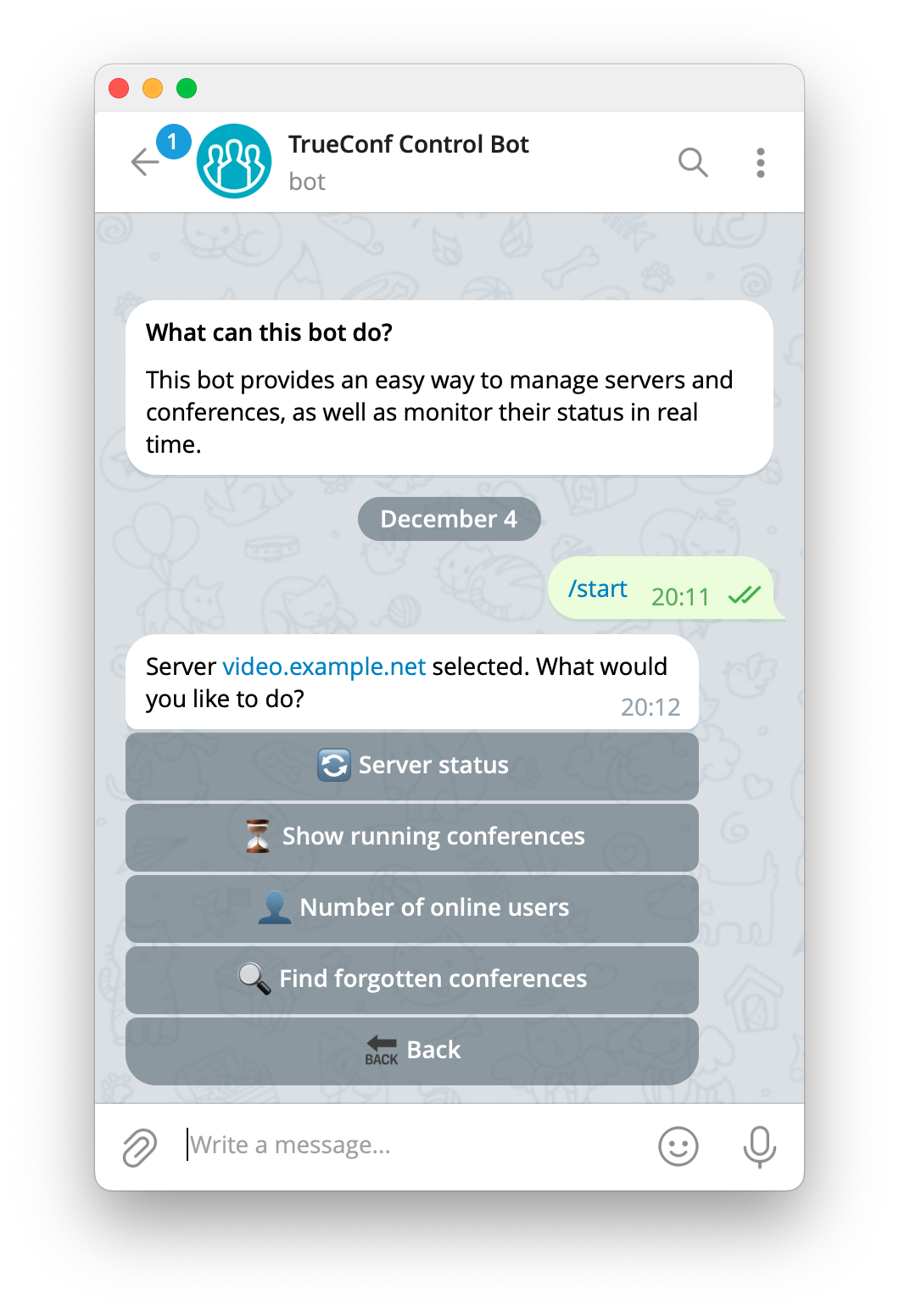
Prerequisites for Launch
For the successful launch of the bot, two conditions must be met:
- Each monitored server must be accessible by its IP address or DNS name from the PC running the bot.
- The PC with the bot must have internet access.
The provided code is an example on which you can base your own bot implementation. Note that the bot’s security is ensured at the OAuth 2.0 protocol and HTTPS level, as well as on the network settings side (access rules, firewall, etc.). The bot operates in long_polling mode, independently polling the Telegram server for new updates. Unlike webhook, this connection scheme is completely secure in a corporate environment.
Registering and configuring your bot
To use the Telegram bot, you will need the official BotFather bot.
BotFather is the only bot that manages bots on Telegram. Read more in the official documentation.
To create a bot:
- Open BotFather and click Run or Start.
- A list of the bot’s commands will appear. You will need the
/newbotcommand. Click on it in the list or send a new message with/newbotto the bot.You can later access the list of available commands by clicking the
Menubutton or simply by typing/in the message input field in the chat with BotFather. - BotFather will then ask you to choose a name for your new bot. Come up with a name, for example,
TCS [name_org], where[name_org]is the name of your organization. - Now, choose a username for your bot. The name must include the word
bot, as it is a requirement from Telegram, for example,server_[name_org]_bot.Please note that the bot’s name and its username are public identifiers that can be used to find it via global search.
- In response, you will receive a message containing information about the created bot and an access token for it via HTTP API in the following format:
Click on the token in the message text to copy it to the clipboard. Then save it in a secure location, as you will need it later to use the bot.15032177032:AAGahjzZ6zbWSEsVFj13Ki-YMPhPEPzQjxE
To access your bot settings, use the /mybots command and select the appropriate username. A menu will open where you can:
- revoke the current token, and a new token is automatically generated;
- edit name, welcome message, description, image;
- add commands.
Now that the bot is configured, you can proceed to launch it.
Preparing the configuration file
First, you need to prepare a configuration file with the access data for your bot and server parameters.
Copy the settings.example.toml file to a new file named settings.toml:
|
1 |
cp settings.example.toml settings.toml |
Now you need to correctly fill in this data structure.
tg-api-token — Telegram HTTP API access token.
tg-users-id — Your numeric Telegram ID. Telegram ensures secure access to the bot using unique user IDs. Therefore, you will need to know your Telegram ID to receive a response from the bot. To obtain it, send any message to the bot @userinfobot.
If you want multiple people to have access to the bot, you can enter their IDs separated by commas.
app/locales folder.
In [servers.<server_name>], replace <server_name> with the preferred server name. It will be displayed in the button names:
ip — The FQDN or IP address of the server.
client_id and client_secret will be available to you after creating an OAuth2 application. For instructions on how to create one, refer to our documentation.
For our example, you will need to select the following permissions in the OAuth application:
- conferences;
- users:read;
- logs.calls:read;
- logs.calls.participants:read.
server_status.state — enables or disables the automatic server availability check. Values: true or false.
server_status.timeout — the time in seconds after which the bot will check the server’s availability (Running, Disconnected). The default is set to 15 seconds, but you can enter your own value.
ssl_certificate — TLS certificate verification setting. If true, each server request will undergo verification. If your server uses a self-signed certificate, specify the path to it in this parameter (use a forward slash /). If the bot is used in a trusted zone (for example, a server located in your corporate network and accessible only by you), specify false to disable certificate verification. If nothing is specified "", it is equivalent to false.
After completing the file, you should have a structure similar to the example below:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
tg-api-token = "12345:example_key" tg-users-id = [12345, 123456] locale = "ru" [servers] [servers."video.example.com"] ip = "video.example.com" client_id = "86add683ebc98123968a549f8976db0024abe288" client_secret = "b7f3f5cb51b02634b1bb546eb7f1f905c93960ba" access_token = "a5bace995fd9d65315f36518fd7b3b4f68a69557" ssl_certificate = "" [servers."video.example.com".server_status] state = true timeout = 15 [servers."video.example.net"] ip = "video.example.net" client_id = "1ebb5498ddd6668d7885c1597f9a1330fc0caddd" client_secret = "067171487c59f063287a44c40671d6247d647e42" access_token = "" ssl_certificate = true [servers."video.example.net".server_status] state = 0 timeout = 15 |
Launching the bot
- Install Python.
- Download the project. On the main page of the repository, click the Code → Download ZIP button and extract the downloaded archive.
- Install pipenv:
1pip install pipenv
- Install the dependencies. To do this, run the following command in the
terminal in the project folder:
where1pipenv install --python 3.x
--python 3.xis your Python version. We recommend using 3.7 and above. - Start the bot:
1pipenv run python3 main.py
When the bot is successfully launched, the terminal will display the message Bot is running…
Deploying the Bot on Cloud Services
You can run your bot not only on a local machine but also in the cloud, which is convenient for continuous operation and accessibility from anywhere. For this purpose, you can use various cloud platforms that offer convenient tools for developing, testing, and deploying applications. Below, we list a few popular services where you can host your bot:
- Replit is a service for running and developing applications directly in the browser.
- Heroku is a platform for deploying and hosting applications with seamless integration with GitHub.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a powerful platform with extensive capabilities for hosting and managing applications.
- AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a cloud platform from Amazon for scalable applications with a multitude of tools and services.
- Microsoft Azure is a platform for developing and managing applications in the cloud with integration into the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Glitch is a service for quick hosting and app development with a simple interface and GitHub integration.
These services allow you not only to deploy a bot but also to scale it easily and ensure its availability to users anywhere in the world.



