Any video conferencing system consists of the following parts:
- Video conferencing endpoints, which can be absolutely any devices that support video and audio transfer: hardware, software or mobile systems, sophisticated telepresence systems or even modernly equipped refrigerators;

- Video conferencing servers, required for group video conferences;
- Infrastructure – communication channels, communication units and secondary equipment for broadcasting and recording video etc.;
- Peripheral equipment – speakerphones, mixers, microphones, PTZ-cameras etc.
Table of Contents
What Modes of Video Conferences Are There?
- Video call, which is a modes of conference that involves connection between two participants. Video conferencing server in this case is optional.
- Group video conference is a multipoint video conferencing session involving three or more subscribers. To create a group video conference, you must have a server that will interchange calls as well as transmit video and audio data. Such group video conferences can be divided into symmetric and asymmetric (video lectures and virtual meetings).
Video Conferencing Server Architecture
All solutions are divided into two groups:
- Hardware solutions, that usually reencode video streams from each participant, which requires a lot of CPU resources.
- Software solutions. They do not reencode video streams and the CPU resources are occupied only for data transmission.
Hardware solutions are often based on modules with DSP-processors to support massive computing. The solutions’ capacity may be increased by adding new modules. Such solutions are more expensive.
Software video conferencing solutions do not require video transcoding, so they can be built on the basis of general-purpose processors. They are much simpler and therefore more accessible.
Types of Video Conferencing System Deployment
- On-premise solution. In this type, all infrastructure is owned and operated by customers themselves.
- Hosted solution. Video conferencing server is located somewhere in the Internet. Video conferencing terminals, in their turn, are located in the customer’s network.
- Managed solution. Servers and client terminals are controlled by the service provider and usually created by the node.js developer.
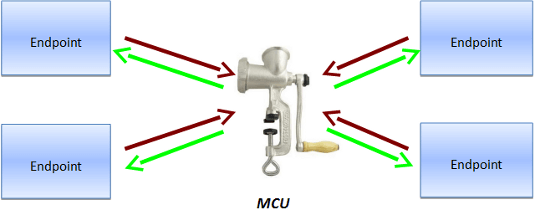
Work Principles of Classical Hardware Video Conferencing Server
MCU (Multipoint Control Unit) accepts video streams from each terminal, decodes and mixes them into one stream, then it encodes and sends the stream to each endpoint.
Hardware Solutions: Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Communication channels efficiency | Requires skilled technical support, because all modern hardware solutions are quite complex and require services of highly qualified and certified professionals. |
| The “weak equipment” problem is eliminated by the use of MCU and scalable video coding (SVC) technology. | Difficulties with scaling. They occur when there is a need to increase the number of servers and users and include system hardware maintenance. |
| Standardized protocols. All hardware solutions were created according to common standards and specifications and due to this they are deeply interoperable. At the very least, audio and video between devices will always be compatible. | Difficulties with enhancements, such as collaboration tools, recording video etc. They also require additional hardware modules, which affects the cost of the system. |
| Centralized management. |
Architecture of Software Video Conferencing Solutions
Software solutions come in various types:
- Client-server solutions, in which communication between endpoints is carried out through a single server. This is a centralized system with good controllability. High reliability of such systems is achieved by duplicating servers. The disadvantage is that all data goes through a single server and the quality of communication depends on the location of the server.
- P2P solutions (peer-to-peer). This is a decentralized system that has high reliability but low controllability. Traffic is routed through various network nodes and connection points (usually endpoints). The disadvantage is that the communication quality may vary along the data path and also depends on the capacity of the nodes.
- Hybrid solutions combine the advantages of the previous types. The endpoints either exchange traffic directly or via a server, depending on the state of communication channels.
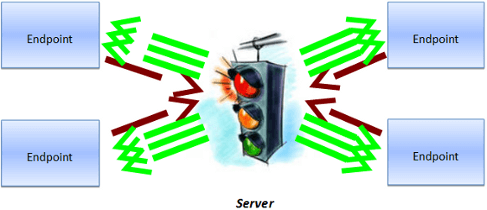
Classical Architecture of PC-Based Video Conferencing
Software platform in such system interchanges incoming streams from participants, replicates them according to the number of receiving participants and sends to each user. Similarly, the use of virtual data room software in business environments can streamline the secure exchange of sensitive information, enhancing collaboration and decision-making processes.
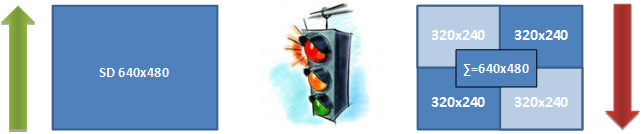
For example, in a symmetric group conference with 4 participants a user who sends video with 640×360 resolution (SD – standard definition), will receive video with resolution of 4x(640×360) = 1280×720 (HD – High Definition).
The user receives the maximum resolution, the sum of the resolutions of all participants of a group video conference.
Improved Architecture of PC-Based Video Conferencing Without Transcoding
Scalable video coding (SVC) technology allows each participant to get the picture, adapted to his/her endpoint. For example, if the endpoint is a smartphone with a 800×480 screen, the 1280×720 resolution would be excessive and so the server reduces the resolution of video streams.
Such solutions are already being released today. Their work is based on video conferencing terminals encoding video in a special way, so that the compressed stream can be divided into several sub-streams of different resolutions or different frame rate without decoding video. Video conferencing server acts as a distributor of quality – it decimates streams according to varying channel conditions or the endpoint capacity, and chooses the most appropriate sub-stream, so that neither you nor your partners have any difficulties in communication.
Ideally, all this allows to fully emulate a hardware MCU on a software-based solution, with the difference that here, instead of recoding, the packets are decimated. This is much more efficient in terms of CPU resources.
What client applications are there?
- Desktop
- Mobile
- In Browser (WebRTC)
- Smart TV Clients
Software Solutions: Pros And Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| It is possible to build a server based on general-purpose processors and standard-based servers. | |
|
Using the existing devices PC serves as an endpoint. |
| The “weak equipment” problem is eliminated by using SVC. | Peripheral equipment must be purchased separately. |
| Easy to scale. It depends on the channel capacity on the server. | |
| All functionality is already in the package |
How to choose the right video conferencing software?
If you’re looking for the best deal for your business and don’t know which provider to turn to, check out detailed comparisons of some of these platforms. Compare