GDPR Compliance in Video Conferencing
During the recent couple of years, virtual meetings evolved into a fundamental element within daily corporate workflows. The expansion of remote plus flexible employment structures has dramatically boosted dependence upon video conferencing ecosystems for strategic cooperation, customer engagement, and also crucial conversations including contract drafting, healthcare exchanges, or even specialized dental credentialing services where sensitive records are involved.
Nevertheless, this swift technological advancement has simultaneously triggered significant debates regarding privacy alongside information protection. Video sessions frequently require transmission of confidential details, archived materials, distributed content, and additionally biometric identifiers such as speech and imagery. Absent adequate precautions, enterprises could reveal valuable records to illegal intrusion, leaks, or exploitation.
This discussion examines methods to guarantee that virtual meetings continue GDPR-compliant. It outlines central doctrines in the legislation, emphasizes important statutory obligations, and delivers actionable recommendations aimed at organizations and participants to secure private information throughout video conferencing and digital recordings.
What is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) represents a binding framework created by the European Union to protect individual information and privacy. It formally came into force on May 25, 2018, and applies across all institutions that manage or retain personal records associated with citizens within the EU.
The scope of GDPR remains extensive, encompassing each procedure linked to the gathering, processing, and transmission of sensitive data. This implies that even if a business operates inside or beyond the EU, it must adhere to GDPR whenever it delivers goods or solutions to EU residents or supervises their digital interactions, including cases where cloud services are used to store or transmit meeting content.
At the foundation of GDPR stand multiple fundamental principles:
- Lawfulness, fairness, and transparency: information should be handled through a lawful, ethical, and comprehensible process.
- Data minimization: just the information absolutely essential for a defined task ought to be obtained.
- Storage limitation: personal records must never be preserved longer than required.
- Confidentiality and integrity: material needs to remain safeguarded from illicit access, modification, or disappearance and ensures reliable data privacy for participants.
In application, GDPR creates a global benchmark for privacy protection that reaches far outside Europe, directing international companies and shaping how they architect, operate, and defend digital infrastructures.
Why is GDPR So Important?
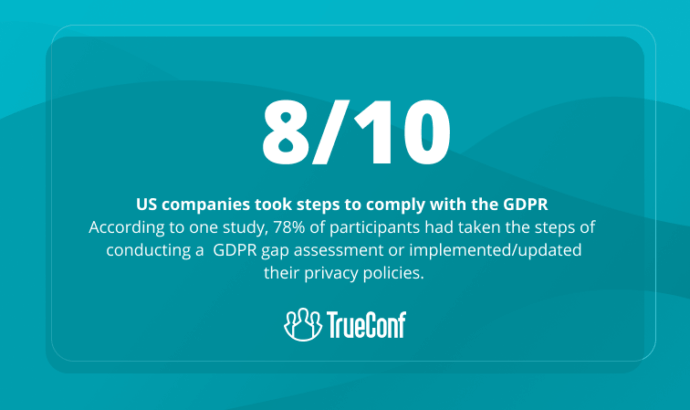
Mishandling personal records presents considerable dangers for enterprises of diverse scales. When delicate information including client credentials, patient histories, or monetary dealings becomes gathered or retained lacking sufficient defenses, the outcomes might involve security leaks, identity fraud, and absence of oversight regarding extremely private material.
Alongside these threats, GDPR establishes rigorous compliance mechanisms. Organizations that neglect to align with its obligations could encounter heavy sanctions and charges, which may climb close to 20 million euros or 4% from the entity’s worldwide yearly revenue, whichever proves greater. These fiscal repercussions may become catastrophic, especially concerning emerging companies and entrepreneurs.
Apart from regulatory and monetary effects, GDPR adherence remains equally essential for preserving confidence and reputation. Consumers, collaborators, and associates demand openness and liability concerning how individual information gets processed. Displaying GDPR alignment conveys accountability and expertise, whereas neglecting such standards could harm credibility, diminish stakeholder reliance, and seriously impact sustained commercial partnerships.
Relevant GDPR Articles for Video Conferencing & Recordings
During managing or documenting online meetings, several elements of the GDPR become particularly significant. These provisions build the framework for legitimate, protected, and open information handling within modern video conferencing.
- Article 5: Principles of data processing
- Article 6: Lawful basis & consent for recordings
- Article 13: Transparency obligations
- Articles 15 & 17: Right of access and erasure
- Article 28: Data Processing Agreements (DPA)
- Article 32: Technical & organizational security measures
Enterprises should guarantee that collected information is processed legally, ethically, and visibly. Data must remain gathered solely for defined, justified purposes, reduced to what proves absolutely required, and preserved only while necessary. Reliability and secrecy must persist consistently.
Digital recordings require establishing a proper regulatory justification. Frequently, this demands obtaining clear authorization from session participants. Notifying attendees beforehand and offering alternatives to refuse recording are essential for adherence.
Attendees should receive precise explanations regarding which information becomes obtained, how it may be utilized, and which parties obtain access. Privacy statements and open announcements throughout meetings are central to compliance.
Individuals hold entitlement to review their personal information and request permanent deletion. Practically, this indicates that companies must prepare to deliver copies of archived sessions or remove participant content if demanded.
Whenever external providers participate in maintaining or analyzing conferencing information, a binding Data Processing Agreement is mandatory. This guarantees processors operate strictly under documented instructions while satisfying GDPR expectations.
Collectively, these provisions design a structure enabling organizations to preserve GDPR compliance across all phases of handling video conferencing and recordings, from configuration and participation through archiving and later elimination.
How to Keep Video Conferencing GDPR-Compliant?
Guaranteeing GDPR consistency across online collaboration platforms requires a multi-layered framework that stresses data defense and individual entitlements. To fulfill these expectations:
- Avoid unnecessary gathering of information and reinforce transparency
- Secure meeting archives with restricted access
- Establish lawful justification for transnational information transfer
Providers alongside organizations must prevent gathering redundant records, whether concerning clients, staff, or associates, for illegitimate motives or exploitation. This recommendation highlights the significance of transparent operational principles during conferencing activities, ensuring that participants’ privacy rights remain safeguarded.
Virtual conferencing recordings should remain safeguarded through comprehensive protections that minimize possibilities of unlawful entry or information breaches. Authorization to approach stored files needs to be restricted to verified personnel, including designated Data Protection Officers.
Whenever performing cross-border record transfers, particularly involving providers located outside the EU or equivalent jurisdictions, enterprises must present appropriate regulatory bases for such exchanges. Preserving protected records throughout international operations becomes essential for upholding compliance obligations.
Security Concerns of Processing Recorded Meetings
Managing archived meetings within GDPR introduces numerous protective challenges that companies ought to resolve to secure personal records. Among the foremost obligations is rigorous access management: solely designated personnel must possess permission to review, alter, or distribute recordings.
Moreover, content separation holds significant importance, guaranteeing that confidential material stays isolated from routine datasets. Advanced identity administration mechanisms, including single sign-on and multifactor verification, additionally minimize chances of illegitimate entry.
Comprehensive audit trails deliver transparency by noting who retrieved archives, at which moment, and under what justification, assisting organizations in reacting to assessments or possible violations. Defined storage schedules are similarly crucial, ensuring that materials get eliminated once their relevance has expired.
Ultimately, the entitlements of individuals should be honored, signifying that participants may request retrieval of their records or insist upon deletion whenever justified. Collectively, these safeguards construct a resilient structure for governing recorded meetings in alignment with GDPR.
Why is TrueConf Server GDPR-Compliant?
TrueConf Server is designed with a strong focus on privacy, security, and data control, making it fully aligned with the core principles of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):
- Self-Hosted Architecture
- Data Minimization and Purpose Limitation
- User Consent and Control
- Access Management and Security
- No Data Transfers Outside the EU
- Audit Logs and Accountability
TrueConf Server gets installed on-site, inside the enterprise’s proprietary IT systems. This guarantees that sensitive records are retained and managed locally, excluding reliance on external cloud services, while providing complete authority over data handling and defense.
The system acquires solely the details essential for conferencing functionality and avoids processing private information for unrelated objectives. All record operations remain transparent and confined to legitimate organizational requirements.
TrueConf equips enterprises with mechanisms to capture and supervise participant consent, aligned with GDPR provisions. Individuals maintain the capability to review, amend, or eliminate their personal details whenever requested.
Entry to confidential information and recordings stays tightly regulated through structured permission levels. All records are encrypted during transmission and within storage, eliminating chances of illegitimate entry or breaches.
Since TrueConf Server operates via localized infrastructure, no sensitive records are transmitted outside the EU/EEA, removing complications and vulnerabilities linked to cross-border data circulation.
TrueConf Server preserves extensive audit trails, permitting enterprises to monitor information-handling activities and validate compliance during inspections.
These considerations should significantly support organizations in selecting a conferencing provider that fully adheres to the General Data Protection Regulation and maintains delicate records as safe as achievable. With TrueConf, personally identifiable information remains continually protected and, above all, GDPR-compliant.
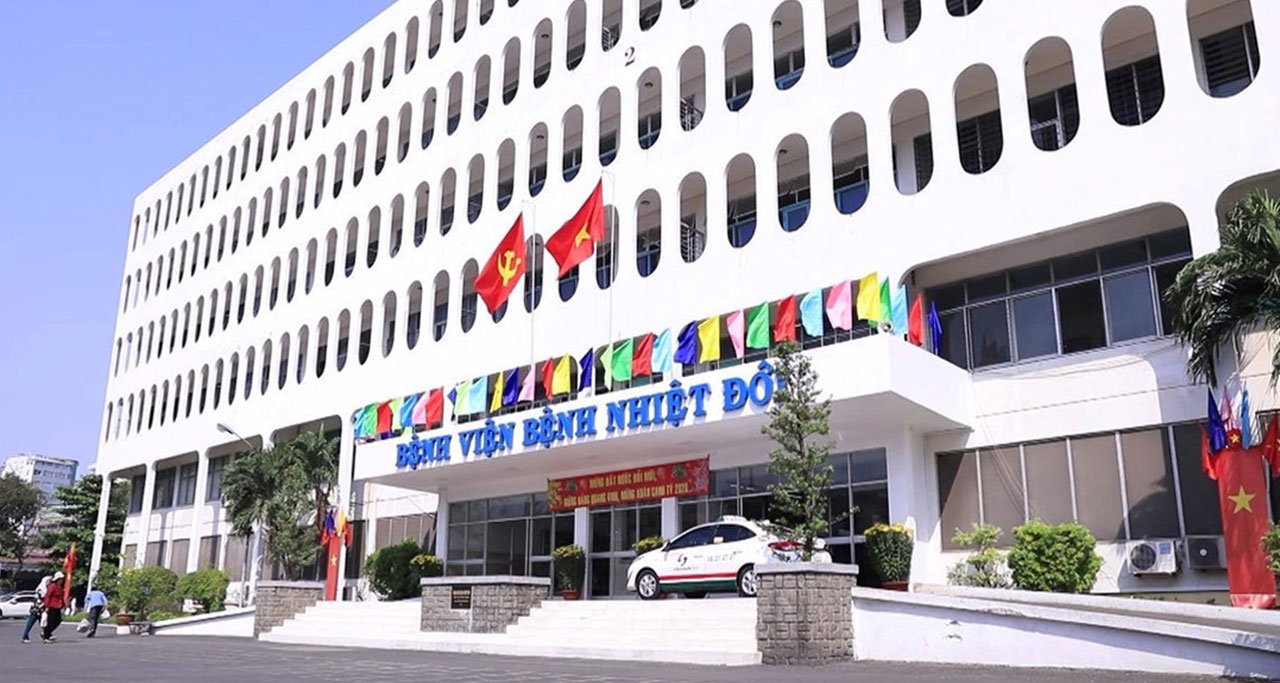
The Department of Health of Ho Chi Minh City|Case Study
TrueConf video collaboration solution connected more than 100 hospitals in Ho Chi Minh and allowed converting quarterly medical examination and treatment briefings between the Department of Health and hospitals into online mode. 660 employees of the City Oncology Hospital can now collaborate with one another without any barriers, increasing both speed and efficiency of communications.

What Can I Do as a User to Ensure Data Protection for Video Conferences?
Participants themselves maintain an important responsibility in guaranteeing that online conferences stay protected and GDPR-compliant. Among the strongest precautions is generating distinct meeting identifiers and avoiding distributing them openly, thereby lowering possibilities of unlawful intrusion. Applying secure passcodes and restricting admission solely to confirmed attendees enhances defenses considerably.
Equally, it remains crucial to notify individuals beforehand whenever a session shall be documented, granting them the chance to refuse or withdraw participation. Exercising care regarding materials displayed throughout discussions reduces unnecessary disclosure: only relevant details ought to appear, and content sharing should remain controlled.
Lastly, attendees need to stay vigilant against hyperlinks, downloads, or sudden notifications within meetings, since these could be exploited through phishing tactics. Through adopting such behaviors, people actively assist in defending personal information while reinforcing reliability in digital collaboration.
Conclusion
GDPR has reshaped how enterprises should manage privacy responsibilities, and online conferencing remains no exception. Digital meetings frequently include the transmission of extremely delicate personal information, which renders consistent adherence with privacy directives indispensable. Through aligning conferencing activities under GDPR, organizations may drastically lower regulatory plus cybersecurity threats while cultivating deeper trust among clients, associates, and employees.
The foundation of effectiveness resides in selecting suitable platforms and adopting reliable strategies. Enterprises ought to choose vendors that emphasize protection, clarity, and information sovereignty, ideally those operating within the EU or providing internal deployment. Simultaneously, participants themselves must undertake preventative measures, including applying distinct session IDs, activating entry codes, and exercising vigilance with recordings, to secure their own safety alongside that of colleagues.
In the end, GDPR conformity functions not merely as statutory necessity but additionally as corporate strength. Businesses that showcase responsibility and defend private information reinforce credibility, increase customer loyalty, and position themselves as dependable actors in today’s increasingly digital environment.
FAQ
Are internal or self-managed conferencing systems practical alternatives?
For institutions processing particularly delicate data, locally hosted or self-managed systems deliver enhanced oversight and resilience. With such configurations, every meeting file, archive, and metadata resides entirely within organizational infrastructure. This reduces dependence upon external vendors, limits vulnerability to third-party threats, and facilitates easier assurance of complete alignment with GDPR responsibilities.
Why should businesses prioritize providers located inside the EU or EEA?
The geographic and regulatory placement of providers proves decisive. Firms operating inside the EU or EEA remain directly bound by GDPR oversight, which enforces tougher compliance with established privacy standards. Selecting vendors situated within Europe decreases exposure to questionable transfers toward regions where protective laws are weaker or inconsistent with GDPR fundamentals.
Why have significant worries emerged about information protection in Zoom?
Zoom has frequently attracted criticism regarding its treatment of consumer information, particularly during initial phases of explosive adoption. Issues included accidental data routing across foreign infrastructures, ambiguous consent handling, and deficiencies in encryption protocols, all creating considerable doubts about whether the platform could maintain conformity with GDPR. These controversies underline the necessity of critically reviewing any provider’s reputation in protecting personal details.
About the Author
Olga Afonina is a technology writer and industry expert specializing in video conferencing solutions and collaboration software. At TrueConf, she focuses on exploring the latest trends in collaboration technologies and providing businesses with practical insights into effective workplace communication. Drawing on her background in content development and industry research, Olga writes articles and reviews that help readers better understand the benefits of enterprise-grade communication.


Follow us on social networks