UVC (USB Video Device Class)
UVC (USB Video Class) is a class of devices that transmit in-stream video over USB. UVC is an evolution of Plug and Play technology, where the initial detection and configuration of a device are performed by the operating system without any user interaction.
With the UVC standard, the host receives structures describing video device functionality and USB queries in order to control various parameters and characteristics of the video stream. UVC also gives video devices the flexibility to support multiple video resolutions, formats, and frame rates, which have a significant impact on bandwidth matching between the device and the host.
Many operating systems, especially those designed for gaming devices, have built-in support for UVC drivers (e.g., PlayStation 3). UVC support significantly reduces the time required for developers to create USB video devices.
Most modern PTZ cameras and common consumer webcams support UVC.
History of UVC
The first version of the specification, UVC 1.0, was released in 2003. UVC 1.5, the current version, was released in 2012. It added support for USB 3.0, as well as H.264 and VP8 codecs with the corresponding management tools.
UVC Advantages
- Users do not need to manually install drivers to enable basic device functionality.
- For video conferencing software developers, UVC simplifies the porting of their products to other operating systems and ensures the same functionality across devices.
- For webcam manufacturers, having a unified specification makes it easier to support and maintain compatibility of their solutions with different operating systems and software products. There is no need to write drivers; it is only necessary to implement UVC support at the hardware level.
USB Video Class Use Cases
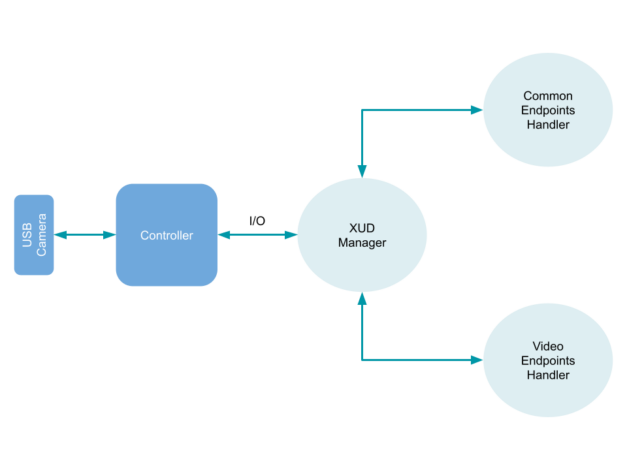
In this example, we will consider how the UVC standard helps develop a device based on XMOS chips designed for the Internet of Things and audio/video devices. The simplest logical workflow for this technology is shown below.
In this case, the XMOS USB device library is used to develop a simple program that can read a USB Video Class device on the host machine. Then this program sends an uncompressed video stream in YUV format at 30 fps to a video capture host software, such as OBS Studio. The xCORE-USB multi-core microcontroller is used as the hardware component.
To process signals from the USB video device, the system performs three tasks running on separate logical cores of the microcontroller:
- The subroutine that implements the USB communication library features (XUD Manager).
- The handler that responds to both standard and specific video class requests (Common Endpoints Handler).
- The process that sends video data to streaming software (Video Endpoints Handler).
These tasks interoperate using XConnect channels, which allow data to be transferred between application code running on separate logical cores. The following diagram shows the tasks and communication structure from this example:
Supported Formats
The following streaming video data profiles are supported in UVC 1.5:
- MJPEG
- MPEG-1 SS
- MPEG-2 PS
- MPEG-2 TS
- MPEG-4 SL
- H.264
- VP8
- SMPTE VC1
- uncompressed YUV formats: YUY2, NV12
- DV formats: SD-DV, SDL-DV, and HD-DV
Supported Operating Systems
|
Operating System |
Support |
|---|---|
|
Windows |
Windows XP SP2+ для UVC 1.0 |
|
|
Windows 7+ для UVC 1.1 |
|
|
Windows 8+ for UVC 1.5 |
|
Linux |
Kernel versions 2.6.26+ for UVC 1.1 |
|
|
Kernel versions 4.5+ for UVC 1.5 (no support for MPEG-2 TS, H.264, and VP8) |
|
macOS |
Mac OS X Tiger (10.4.3)+ |
|
FreeBSD |
9.0+ |

Follow us on social networks